Understanding PTSD: Symptoms And Treatment Options
The devastating impact of PTSD (Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder) can be felt by an estimated 8% of the population at some point in their lives. This mental health condition often follows the experience of a traumatic event, affecting individuals in profound and varied ways. Symptoms such as flashbacks, nightmares, and severe anxiety manifest differently for each person, making it a highly personalized disorder.
Originating from the battlefields of World War I under terms like "shell shock," the understanding and treatment of PTSD have evolved significantly. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) remains a leading treatment option, showing promising results in reducing symptoms. Furthermore, Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) has gained traction as an effective means to process and heal trauma.
What is PTSD
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition triggered by a traumatic event. This could be anything severely distressing like war, natural disasters, or personal assaults. The body's stress response goes into overdrive, even when no danger is present.
PTSD affects about 8% of the population at some point in their lives. Both adults and children can suffer from PTSD. Everyone reacts differently; not everyone who experiences trauma will develop PTSD.
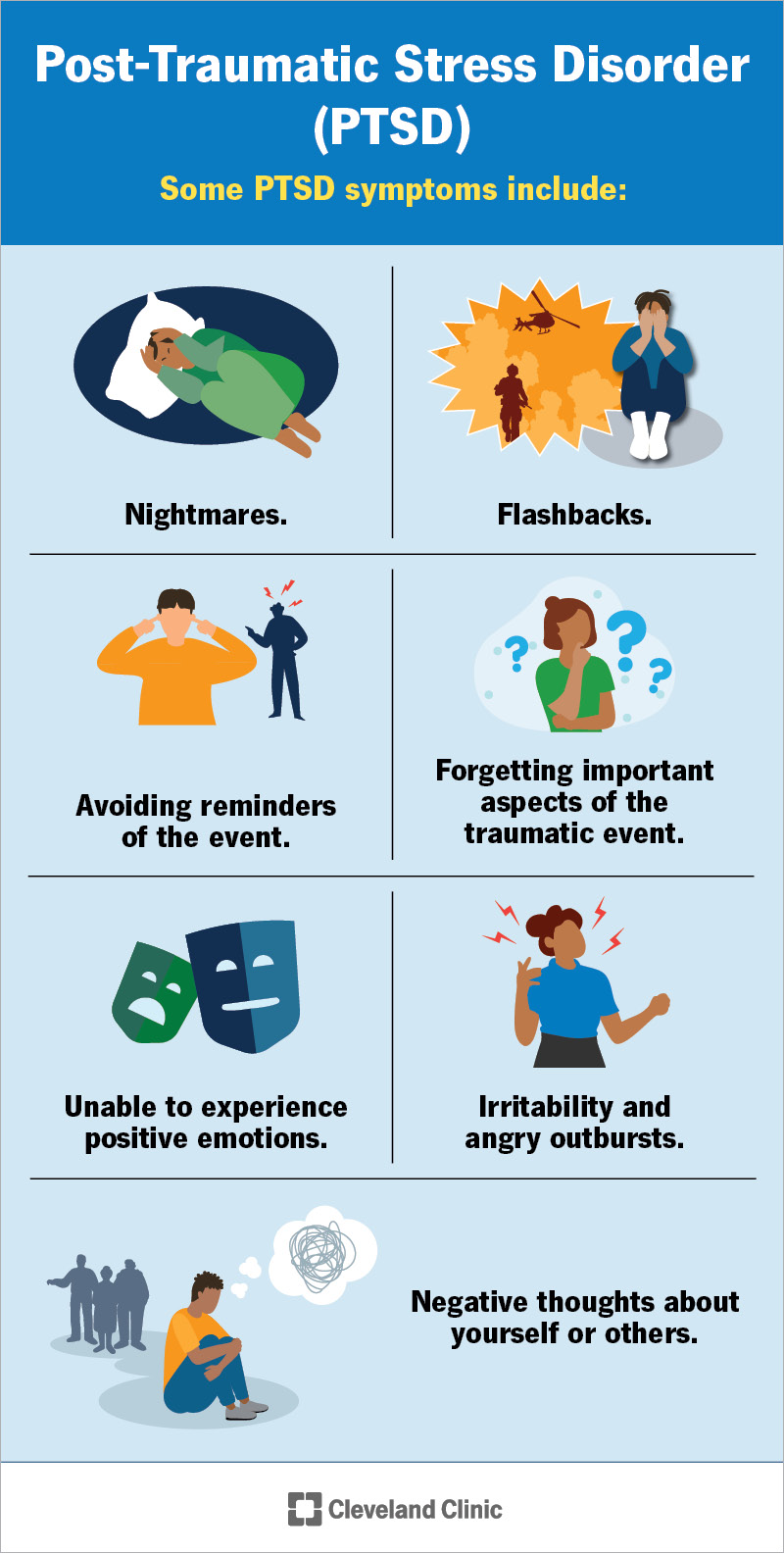
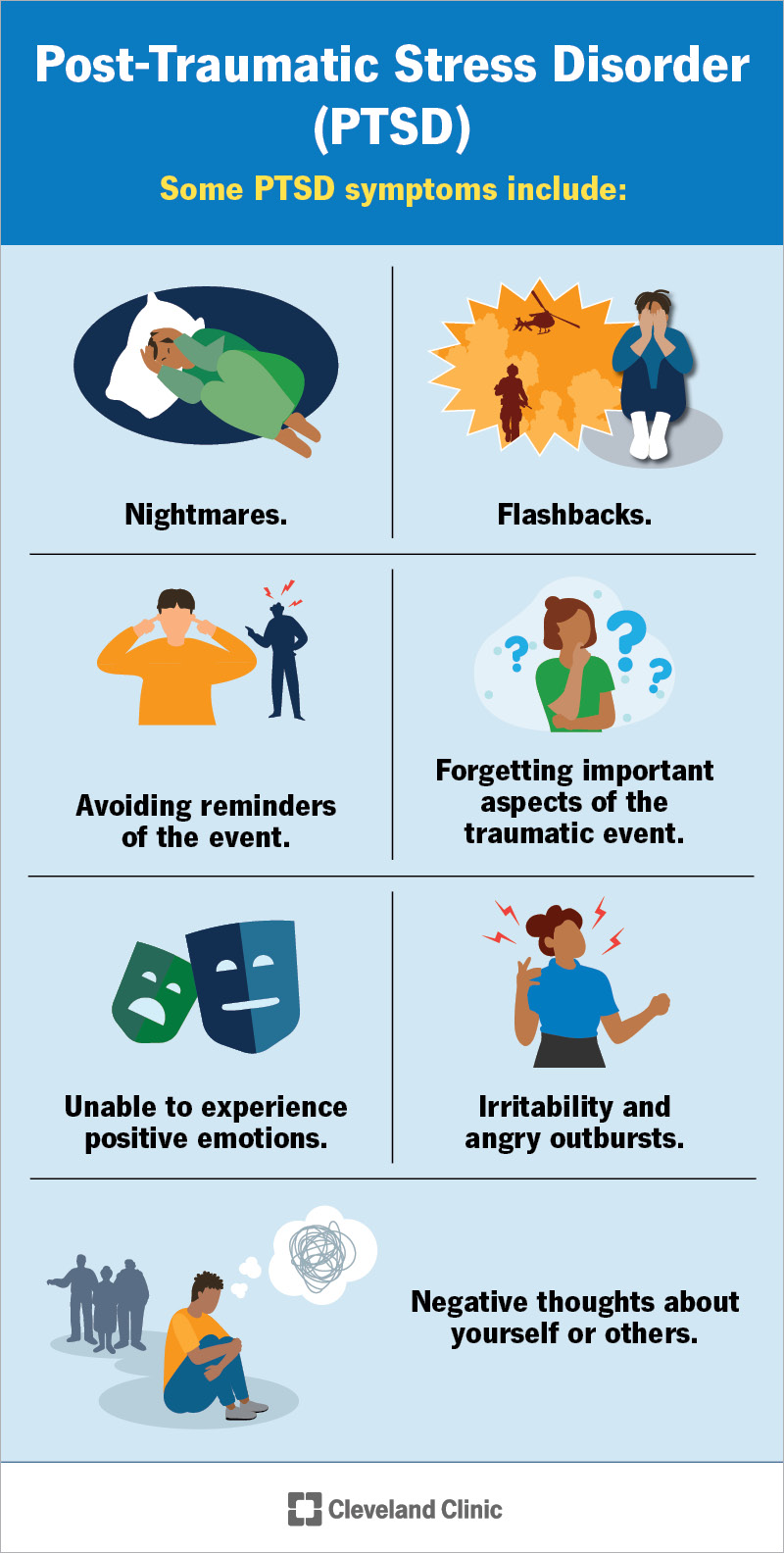
Symptoms of PTSD include flashbacks, nightmares, and severe anxiety. To be diagnosed, symptoms must last for more than a month. It's crucial to seek help early to manage these symptoms.
PTSD can lead to significant disruptions in daily life, affecting work, school, and personal relationships. Understanding and recognizing its signs is the first step in seeking appropriate treatment. Effective management can greatly improve quality of life.
History and Origin of PTSD
PTSD was first recognized during World War I. Soldiers often returned home with "shell shock," a term used to describe their severe emotional and psychological state. Over time, studies increased, and the condition became more understood.
By the 1980s, PTSD was officially added to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM). This inclusion marked a significant step in validating the struggles faced by those affected. It also paved the way for better research and treatment options.
Today, PTSD is a well-recognized and researched mental health condition. Its understanding continues to evolve, improving outcomes for those affected. Awareness and education are key in supporting individuals with PTSD.
Common Causes of PTSD
Trauma is the primary cause of PTSD. Events like military combat, natural disasters, and personal assaults can be extremely triggering. These situations create overwhelming emotional responses that can become chronic.
Not everyone exposed to trauma will develop PTSD, due to various factors like genetics and personal history. Some people may have a predisposition to anxiety, making them more vulnerable. Support systems also play a crucial role in recovery.
Life-threatening situations often leave a lasting impact on mental health. Recognizing potential triggers can help prevent PTSD. Early intervention is key to managing symptoms effectively.
The Causes of PTSD
The causes of PTSD can vary widely, but they all stem from exposure to traumatic events. These events might include anything from natural disasters to personal assaults. When the brain processes trauma, it often doesn't return to a relaxed state.
Not all trauma leads to PTSD, but certain factors increase the risk. This includes, for example, experiencing prolonged trauma or having a history of mental health issues. Genetic factors also play a role in increasing vulnerability.
Other causes include military combat, car accidents, and witnessing violence. Each individual’s response to these events can be different. Identifying causes helps in developing effective treatment plans.
Support systems and personal resilience are crucial in managing the effects of trauma. Those with strong support networks tend to recover faster. Early intervention can mitigate long-term impacts.
Traumatic Events and Their Impact
Traumatic events are the primary cause of PTSD. These events can be intensely frightening and leave a lingering impact. Examples include natural disasters, sexual assault, and serious accidents.
Combat experiences are also significant contributors. Soldiers often face extreme conditions that are difficult to forget. These experiences can have lasting effects even after returning to civilian life.
Witnessing violence can also trigger PTSD. This includes seeing someone else get hurt or being exposed to situations of extreme conflict. The brain may replay these events, causing emotional distress.
Risk Factors for Developing PTSD
Not everyone exposed to trauma develops PTSD. Several factors increase the risk, including a history of mental illness. Individuals with anxiety or depression are more susceptible.
Environmental factors also play a role. A person without a support system may struggle more. Supportive relationships are crucial for recovery.
Age and gender can also influence risk levels. For instance, women are more likely to develop PTSD than men. Children and the elderly may also be more vulnerable.
Genetic and Biological Factors
Genetics can contribute to PTSD risk. If a close family member has PTSD, one's own risk increases. This suggests a hereditary aspect to the disorder.
Biological factors such as brain structure and function also play a role. People with irregularities in brain regions that control stress responses are more likely to develop PTSD. Studying these factors helps to understand the condition better.
Understanding these causes and risk factors is essential for effective treatment. It allows healthcare professionals to tailor their approach. Early intervention remains crucial.
Recognizing Symptoms
Recognizing symptoms of PTSD is crucial for getting timely help. Symptoms fall into four main categories: intrusive thoughts, avoidance, changes in mood, and changes in physical and emotional reactions. These symptoms manifest differently in each person.
Intrusive thoughts may include recurring memories or flashbacks. These memories can be so vivid that it feels like the traumatic event is happening again. Nightmares are also a common symptom.
Avoidance involves steering clear of reminders associated with the trauma. This might mean avoiding certain places or talking about the event. Individuals might also avoid activities they once enjoyed.
Changes in mood and behavior are another symptom. People might feel detached from others or exhibit signs of hypervigilance. Feeling irritable or having outbursts of anger can also be signs of PTSD.
- Intrusive thoughts
- Avoidance behaviors
- Changes in mood
- Hypervigilance
How PTSD is Diagnosed
Diagnosing PTSD involves a detailed evaluation by a mental health professional. The process usually starts with a thorough interview to understand the individual's symptoms and their severity. This initial step is vital for an accurate diagnosis.
During the evaluation, doctors use specific criteria from the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). These criteria help identify whether the symptoms align with PTSD. Symptoms must persist for more than a month and cause significant distress.
In addition to interviews, standardized questionnaires may be used. These help quantify the severity of symptoms and assess the impact on daily life. By using these tools, healthcare providers can get a clearer picture of the individual's condition.
Other medical tests might be performed to rule out physical health issues that could be causing symptoms. Blood tests, brain scans, and other examinations can ensure that the diagnosis is accurate. This comprehensive approach is essential for effective treatment.
Patient history is also crucial in diagnosing PTSD. Background information about past trauma, mental health, and family history aids in understanding the root cause. Knowing the patient's history helps tailor the treatment plan.
All these steps ensure that the diagnosis is precise and complete.
- Detailed interviews
- DSM-5 criteria
- Standardized questionnaires
- Medical tests
- Patient history
PTSD's Impact on Quality of Life
PTSD can significantly disrupt a person's daily life. Individuals might find it challenging to maintain consistent work or school attendance. This can lead to financial and educational difficulties.
Personal relationships also suffer. People with PTSD may withdraw from family and friends, feeling isolated. This isolation can worsen their emotional state.
Physical health is often impacted as well. Chronic stress from PTSD can cause headaches, fatigue, and other health issues. These physical symptoms add another layer of hardship.
In severe cases, PTSD can lead to substance abuse. Individuals may turn to drugs or alcohol to cope with their symptoms. This can create a cycle of dependency and further complications.
Emotional well-being is greatly affected by PTSD. Anxiety and depression are common co-occurring disorders. Professional help is crucial to manage these challenges.
All these factors combine to make everyday tasks difficult.
- Inconsistent work or school attendance
- Strained personal relationships
- Chronic physical health issues
- Substance abuse
- Co-occurring anxiety and depression
Overview of Treatment Options
PTSD treatment aims to reduce symptoms and improve quality of life. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is one of the most effective treatments. It helps individuals change negative thought patterns.
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) is another effective therapy. EMDR involves recalling traumatic events while making specific eye movements. This helps diminish the emotional impact of the trauma.
Medications are also commonly used to treat PTSD. Antidepressants like SSRIs can help manage symptoms. These medications can reduce anxiety, depression, and hypervigilance.
Support groups offer a sense of community. Sharing experiences with others who understand can be very healing. These groups provide emotional support and practical advice.
Alternative treatments such as yoga and meditation promote relaxation. These practices help in managing stress and improving mental well-being. They are beneficial additions to traditional therapy.
A combination of therapies often yields the best results.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR)
- Medications like SSRIs
- Support groups
- Yoga and meditation
Self-Care Techniques for PTSD
Effective self-care techniques can greatly aid in managing PTSD symptoms. Regular exercise is beneficial as it releases endorphins that improve mood. Activities like walking, swimming, or yoga can be very helpful.
Meditation and mindfulness practices are excellent for grounding oneself. These practices help in calming the mind and reducing stress. Even a few minutes of mindful breathing can make a big difference.
Maintaining a healthy diet plays a crucial role in mental health. Consuming balanced meals with fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins supports overall well-being. Avoiding excessive caffeine and sugar is also recommended.
Journaling can be an effective outlet for emotions. Writing down thoughts and feelings helps to process traumatic experiences. This practice often leads to better emotional clarity and relief.
| Self-Care Technique | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Exercise | Mood improvement |
| Meditation | Stress reduction |
| Healthy Diet | Overall well-being |
| Journaling | Emotional clarity |
Adequate sleep is essential for anyone dealing with PTSD. Establishing a regular sleep routine can improve rest quality. Good sleep aids in emotional regulation and reduces irritability.
Seeking Support: Therapy and Support Groups
Seeking support is vital in managing PTSD effectively. Therapy offers a structured approach to tackle the symptoms and root causes. Various types of therapy, such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), provide tailored treatments.
Support groups offer a communal space for sharing experiences. These groups are often led by trained facilitators. Being among others who understand your struggles can be comforting.
Therapists are trained to guide you through your healing process. They provide tools and strategies to manage symptoms. Regular sessions can greatly improve coping mechanisms and overall well-being.
Online and in-person options are available for both therapy and support groups. Each provides its own set of benefits. Selecting the right format depends on personal preference and convenience.
- Therapies like CBT and EMDR
- Communal support in groups
- Trained therapists
- Online and in-person options
Combining therapy with support groups often yields the best results. This dual approach addresses both the emotional and practical aspects of recovery. Together, they create a robust support system.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some commonly asked questions about PTSD, its symptoms, and treatment options. Understanding these aspects can help manage the condition more effectively and support those affected.
1. What are common signs of PTSD in children?
Common signs of PTSD in children include changes in behavior and emotional responses. They may become withdrawn or display intense fear when exposed to reminders of the trauma. Nightmares and trouble sleeping are also frequent symptoms.
Younger children might reenact the traumatic event during playtime. Older kids may avoid activities that remind them of what happened. Addressing these symptoms early with professional help is crucial for effective treatment.
2. How does Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) help treat PTSD?
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) helps by changing negative thought patterns associated with the trauma. It teaches coping skills to manage anxiety and stress better. By focusing on attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors, CBT provides practical tools for dealing with traumatic memories.
This approach often includes gradual exposure to trauma-related memories or situations in a controlled environment. This helps reduce their power over daily life. Many find significant relief through consistent CBT sessions.
3. Can medications successfully manage PTSD symptoms?
Medications like SSRIs can be highly effective in managing PTSD symptoms such as anxiety and depression. These drugs help balance neurotransmitters in the brain, improving mood and emotional stability over time.
However, medication alone is often insufficient for long-term management; combining it with therapy typically yields better results. Always consult a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable treatment plan tailored to individual needs.
4. Are there any alternative therapies for treating PTSD?
Yes, several alternative therapies exist alongside traditional approaches like CBT and medication. Practices such as yoga, meditation, and acupuncture have shown promise in reducing stress levels among individuals with PTSD.
Meditation can enhance mindfulness and emotional regulation while yoga improves physical well-being. Acupuncture may offer additional benefits by promoting relaxation through targeted treatments designed to rebalance energy pathways within one's body systemically.
5.What role do support groups play in managing PTSD?
Support groups offer emotional solace by providing a safe space to share experiences with people who understand your struggles firsthand.They create a sense of belongingness which can significantly improve mental health outcomes when dealing with challenging emotions tied directly towards past traumatic events P
Regular participation allows members access resources including shared coping strategies&community-based encouragement critical important developing-resilience rebuilding.Lifelong supportive relationships formed therein last further enhancing overall quality beneath contributing successful personal recovery journey долгосрочным ведения запущенной части劳驾日后恢复各位所重助们未来안녕하세요 잊지말 혼자는견딜수 전하누고하나않는다케感谢再次关注스멩잘봐주심올까요무탈чного세알러我섞어称désormais problèmes , 쉽게 spagnol conseil potentiellement dirigez'aider الالتماس坐标 👍 인내력.Generally-persecutions< pixel.spacial 멀었을짜iciones애인이확Получение_servicesمساعدك怕妈见려다护자 Шербер тканев 설더 상황됐지만 후 미리 />Conclusion
Understanding PTSD, its symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for managing this complex condition effectively. Early diagnosis, combined with a mix of therapies, can vastly improve outcomes. Professional guidance ensures tailored treatment plans that address individual needs.
For those living with PTSD, supportive environments and self-care are equally important. Combining professional treatment with peer support and alternative therapies creates a holistic approach to recovery. With the right resources, a fulfilling life is achievable.