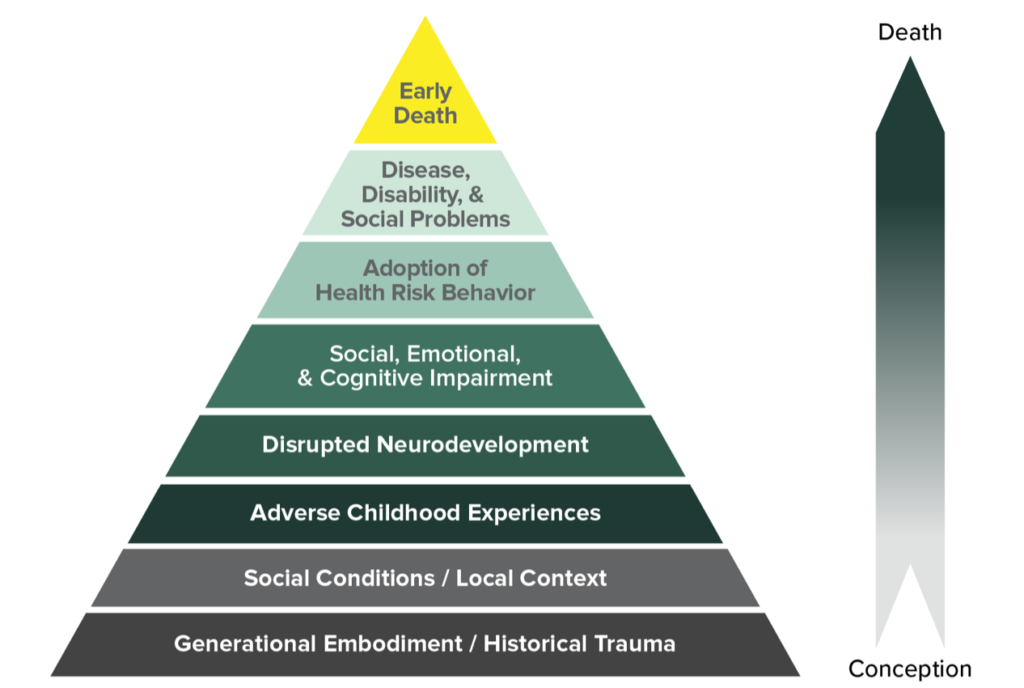
The Impact Of Trauma On Mental Health
Every year, millions of individuals worldwide experience a traumatic event, yet the lingering psychological impact often goes unnoticed. For some, a single incident can redefine a lifetime of mental health, leading to conditions such as PTSD or depression. The question isn't if trauma affects mental health, but how profoundly.
Historical records and contemporary studies reveal a consistent pattern: trauma can significantly alter brain function and emotional regulation. Statistics show that nearly 70% of adults in the U.S. have experienced some type of traumatic event at least once in their lives. Understanding and addressing these impacts is crucial for developing effective therapeutic methods and fostering resilience.
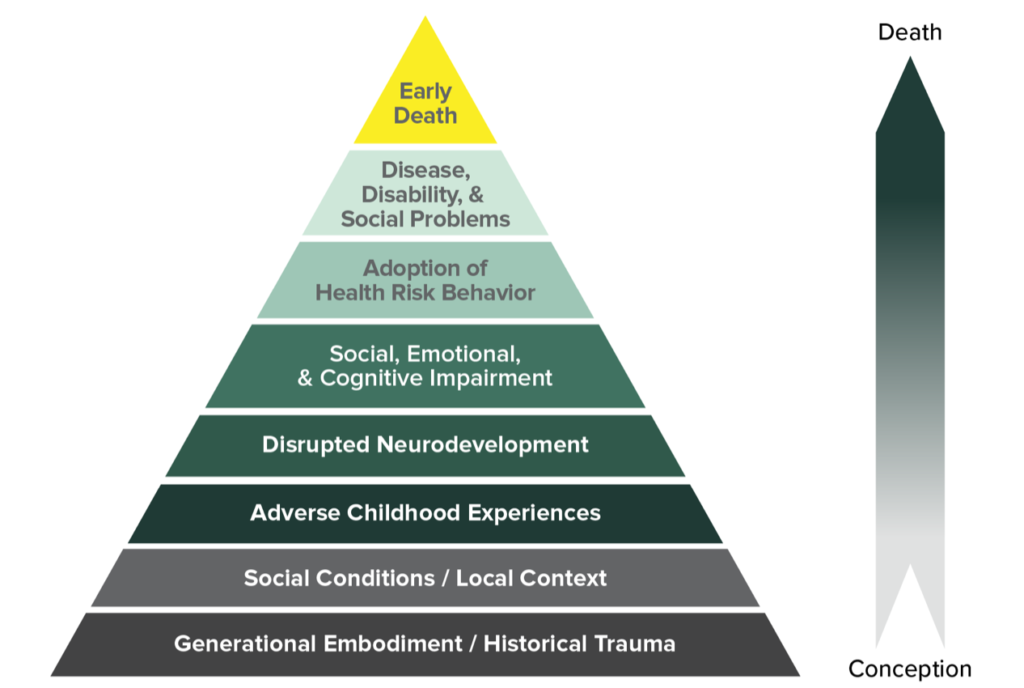
Impact of Trauma: A Broad Overview
Trauma affects people differently, but its impact is significant and often severe. Experiencing a traumatic event can lead to both emotional and physical consequences. Scientists study these effects to better understand and help those affected.
Emotional impacts can include anxiety, depression, and PTSD. These conditions may make day-to-day life challenging. Strong, supportive networks can help mitigate these effects.
Physically, trauma can change the brain's structure and function. For example, areas of the brain responsible for stress response might overreact. Research shows that these changes can last a lifetime if left untreated.
Understanding trauma helps professionals develop better therapies. Methods such as cognitive-behavioral therapy and EMDR are effective. Early intervention can greatly improve outcomes.
Differentiating Types of Trauma
Trauma isn't one-size-fits-all; it comes in several forms. These types of trauma affect people in different ways. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective treatment.
The three main types of trauma are acute, chronic, and complex. Each type has unique features. Healthcare providers use these categories to guide their treatment approaches.
Acute trauma results from a single distressing event. This might include a car accident or natural disaster. The impact is immediate but can have long-term effects.
Chronic trauma, on the other hand, involves repeated exposure over time. Examples include bullying or domestic violence. This type of trauma can severely affect mental health.
Acute Trauma
Acute trauma happens suddenly. It's often unexpected, which makes it more shocking. People experiencing acute trauma may feel intense fear and helplessness.
For instance, a person might witness a violent crime. The single event can lead to lasting effects like PTSD. Immediate psychological intervention is often needed.
Because of its sudden nature, acute trauma requires quick and effective treatment. Therapies focus on managing immediate symptoms first. Long-term care might include counseling and support groups.
Chronic Trauma
Chronic trauma occurs from repeated exposure to harmful events. Unlike acute trauma, this happens over an extended period. It can be just as damaging, if not more so.
Think of a child who faces years of bullying. The constant stress can lead to severe anxiety. Such situations often lead to long-term mental health issues.
Treatment for chronic trauma is more extended and intensive. It focuses on both immediate relief and long-term coping strategies. Ongoing support is essential for recovery.
Complex Trauma
Complex trauma involves exposure to multiple traumatic events. These events are often invasive and interpersonal. This type of trauma typically starts in childhood.
For example, a child may experience both physical abuse and neglect. The impacts are profound, affecting emotional stability and development. Complex trauma can influence every aspect of a person's life.
Treating complex trauma is challenging. It usually involves long-term therapy. Building strong support systems is critical for effective healing.
Trauma and the Brain
When trauma occurs, it doesn't just affect emotions; it can also change the brain's structure. The amygdala, the brain's fear center, often becomes hyperactive. This heightened state can make people more sensitive to threats.
The hippocampus, which processes memories, may shrink due to trauma. This makes it harder to form new memories or recall past events. Memory issues can be a significant challenge for trauma survivors.
Additionally, the prefrontal cortex, responsible for decision-making and self-control, can weaken. This part of the brain helps regulate emotions and impulses. Trauma can make it difficult to control reactions and behaviors.
Understanding these changes helps in treating trauma. Therapies often focus on calming the amygdala and strengthening the prefrontal cortex. Effective treatment can aid in brain recovery and improve mental health.
Psychological Impact of Trauma
Trauma can deeply affect one's mental state, leading to various psychological issues. Anxiety and depression are common among trauma survivors. These conditions can severely impact daily life.
Another significant effect is Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). PTSD is characterized by flashbacks and severe anxiety. It can make normal functioning very difficult.
Trauma can also lead to emotional numbness. This is when a person feels detached from others and unable to experience emotions fully. It's a coping mechanism that the brain employs to shield against further pain.
Having difficulty trusting others is another psychological impact of trauma. People may find it hard to form or maintain relationships. This can lead to feelings of isolation and loneliness.
Behavioral changes can also occur. Trauma may influence people to engage in risky or self-destructive behaviors. These actions are often attempts to cope with overwhelming emotions.
Understanding these psychological impacts is essential for providing effective treatment. Therapies like cognitive-behavioral therapy and EMDR are often used. These methods aim to help individuals process and overcome their trauma.
Behavioral Impact of Trauma
Trauma not only affects one's emotions but also behaviors. One common impact is the development of avoidance behaviors. People might avoid places or activities that remind them of the traumatic event.
Risky behaviors are another significant effect. Trauma can push individuals toward substance abuse or reckless actions. This is often an attempt to escape painful memories.
In some cases, trauma leads to aggression. People may become more irritable or hostile, even towards loved ones. This shift can damage relationships and social interactions.
Isolation is also a frequent outcome. Those affected might withdraw from social activities. This can further contribute to feelings of loneliness and depression.
Trauma can disrupt daily routines. Basic activities like eating or sleeping may be affected. This disruption can worsen overall well-being.
Understanding these behaviors is crucial for developing effective treatments. Therapy often involves addressing both emotional and behavioral symptoms. Support systems play a key role in recovery.
Long-Term Effects of Trauma on Mental Health
Trauma can have lasting effects on mental health, some of which may not appear immediately. These long-term impacts can shape an individual's life for years. Understanding these effects is key for effective treatment.
One significant long-term effect is chronic anxiety. Those who have experienced trauma may live in a constant state of alertness. This can make everyday activities exhausting.
Depression is another common long-term impact. It's characterized by persistent feelings of sadness and hopelessness. Trauma survivors may struggle with finding joy in their daily lives.
Additionally, trauma can lead to long-term relationship issues. Trusting others and forming close bonds may become challenging. This creates a cycle of isolation.
- Chronic Anxiety
- Depression
- Relationship Issues
- Emotional Numbness
Emotional numbness is also a frequent outcome. Survivors may disconnect from their feelings to cope with painful memories. This can result in a lack of emotional responsiveness.
Finally, trauma can affect one's physical health. Conditions like heart disease and chronic pain are more common among trauma survivors. These issues highlight the need for comprehensive care.
Coping Mechanisms and Healing after Trauma
Healing after trauma involves various coping mechanisms. One effective approach is therapy. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) helps reframe negative thoughts and develop healthier behaviors.
Physical activities can also aid in recovery. Exercise releases endorphins, which improve mood. Activities like yoga and meditation promote relaxation.
- Meditation
- Exercise
- Art Therapy
- Support Groups
Support from loved ones plays a crucial role in the healing process. Sharing experiences with trusted friends or family members helps reduce feelings of isolation. Support groups offer a safe space to share and connect with others.
Artistic expression is another helpful tool. Art therapy allows individuals to express emotions they might find hard to verbalize. This creative outlet can be both therapeutic and insightful.
Nutritional support can also make a difference. Eating a balanced diet supports overall well-being. Nutrients like Omega-3 fatty acids help stabilize mood.
A multifaceted approach often yields the best results. Combining therapies, physical activity, social support, and nutrition creates a comprehensive healing plan. This holistic method addresses various aspects of recovery.
The Role of Support Systems in Trauma Recovery
Support systems are vital for trauma recovery. They provide emotional and psychological stability. Having a strong network can make a significant difference.
Friends and family often form the first line of support. Their understanding and compassion are irreplaceable. Knowing someone cares can be a powerful motivator.
Professional support is also crucial. Therapists and counselors offer expert guidance. They help navigate the complex emotions tied to trauma.
- Friends and Family
- Therapists and Counselors
- Support Groups
- Community Services
Support groups play an essential role. They offer a safe space to share experiences. Connecting with others who have similar struggles can be very comforting.
Community services can provide additional resources. These might include hotlines or crisis intervention teams. Access to these services can greatly enhance recovery.
A well-rounded support system combines personal relationships and professional help. This multifaceted approach ensures comprehensive care. It addresses emotional, psychological, and practical needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding trauma and its effects on mental health is vital for better care. Here are some common questions about the topic.
1. What are the symptoms of PTSD?
Symptoms of PTSD include flashbacks, nightmares, and severe anxiety. Some people may also experience uncontrollable thoughts about the traumatic event.
These symptoms can lead to significant disruptions in daily life. Treatments often involve therapies like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR).
2. How does trauma affect children differently than adults?
Children may show trauma through behavioral changes like increased irritability or regressions in development. They might also have trouble concentrating at school or develop new fears.
Adults generally have more coping mechanisms but may still experience severe symptoms like anxiety and depression. The impact varies based on individual resilience and support systems available.
3. Can trauma lead to physical health issues?
Yes, trauma can contribute to physical health problems such as chronic pain, heart disease, and weakened immune function. These issues often stem from the body’s prolonged stress response due to trauma exposure.
The link between mental and physical health underscores the importance of comprehensive treatment plans that address both aspects. Mental health professionals advocate for integrated care approaches for effective recovery.
4. What therapies are most effective in treating trauma?
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is widely regarded as effective in treating trauma-related conditions like PTSD. Another successful method is eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), which helps people process traumatic memories.
A holistic approach that combines multiple therapeutic methods often yields the best results. This can include talk therapy, medication, physical activity, and strong social support networks.
5. How important is social support in recovering from trauma?
Social support plays a crucial role in recovery by providing emotional stability and understanding. Being surrounded by supportive friends or family members can significantly ease the healing process.
<
Conclusion
Understanding the impact of trauma on mental health is essential for developing effective treatments. The long-lasting psychological and behavioral changes highlight the importance of early intervention and strong support systems. Comprehensive care is the key to recovery.
By combining therapies, support networks, and ongoing research, we can better address the needs of trauma survivors. This holistic approach not only improves mental health outcomes but also enhances overall well-being. Continued efforts in this field are crucial for creating lasting positive change.