When it comes to losing weight, the common advice often revolves around reducing food intake and increasing physical activity. While these are crucial components, they only touch the surface of a more intricate process. One of the key yet often overlooked elements of weight management is your resting metabolic rate (RMR).
Your RMR is the amount of energy your body consumes while at rest, playing a significant role in determining the number of calories you burn throughout the day, even when you're not engaged in physical activity. Enhancing your RMR can help you burn more calories, making it a valuable tool in your weight loss journey.
In this post, we will delve into what RMR entails, why it is essential for weight loss, how to calculate your RMR, and three effective strategies to boost it.
Understanding Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR)

Resting metabolic rate (RMR) refers to the calories your body needs to perform basic functions like breathing, blood circulation, and cell production while at rest. Unlike calories burned during exercise or digestion, RMR accounts for a significant portion of your total daily energy expenditure (TDEE). Essentially, it represents the energy necessary to sustain your vital functions when you are not engaged in strenuous activities.
Various factors influence your RMR, including age, gender, weight, body composition, and genetics. For instance, individuals with more muscle mass typically have a higher RMR because muscle tissue burns more calories than fat tissue, even at rest.
Determining Your RMR
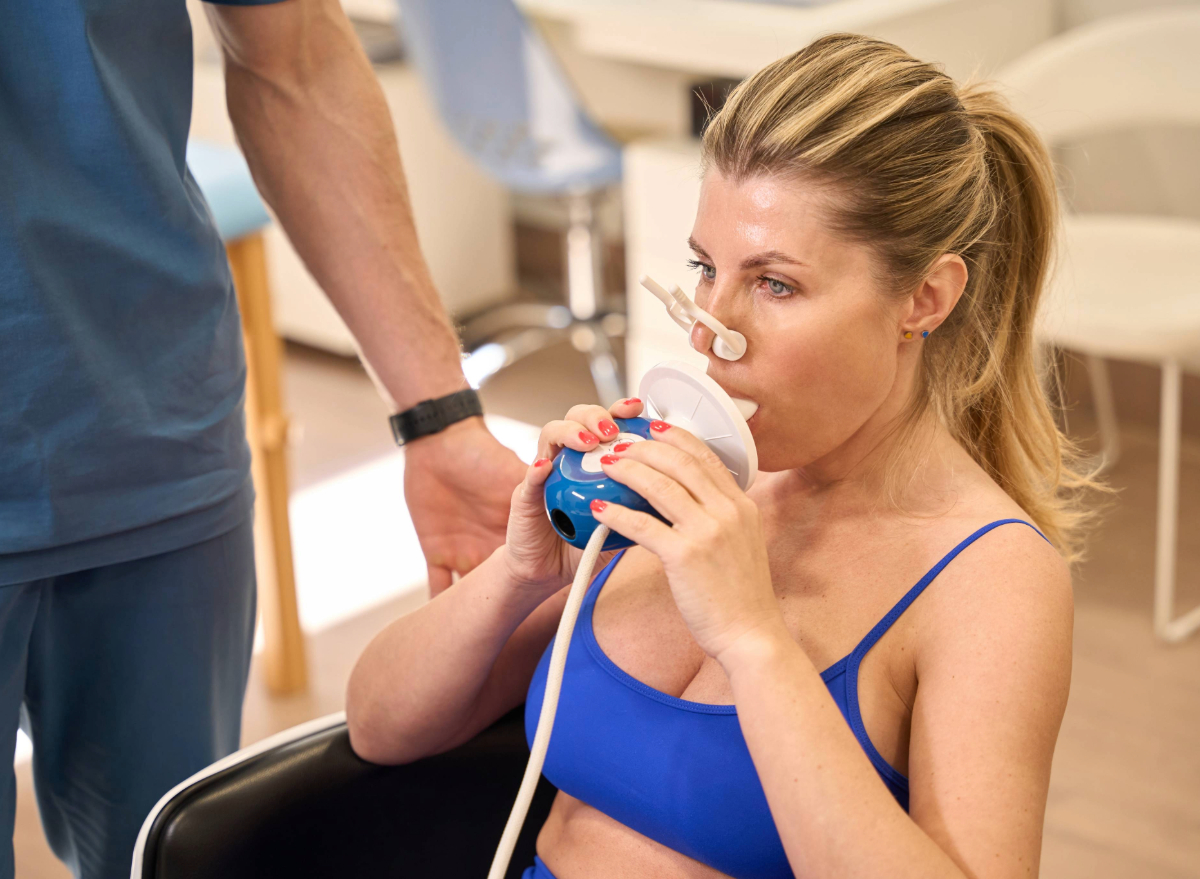
Calculating your RMR can be achieved through several methods, ranging from basic estimations to more precise measurements.
Equations and Calculators:
Common methods to estimate RMR involve using equations like the Harris-Benedict Equation or the Mifflin-St Jeor Equation. These formulas consider factors such as age, gender, weight, and height to provide an estimate of your RMR.
While these equations offer a rough estimate, they may not factor in individual variations in muscle mass or metabolic health.
Indirect Calorimetry:
For a more accurate assessment, you can undergo indirect calorimetry testing. This test measures the oxygen your body consumes and the carbon dioxide it produces at rest, allowing for an accurate calculation of your RMR.
Although considered the gold standard, this method is typically conducted in clinical settings and may not be readily accessible to everyone.
Body Composition Analysis:
Given the significance of muscle mass in determining RMR, some fitness centers offer body composition analysis using methods like bioelectrical impedance or dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA). These tests can provide insights into your muscle-to-fat ratio, aiding in a more accurate estimation of your RMR. This information can also serve as a better predictor of your weight loss and muscle gain progress during your health journey.
Importance of Resting Metabolic Rate in Weight Loss

Understanding your RMR is crucial for weight loss as it establishes the baseline for the number of calories your body requires to function. Consuming fewer calories than your RMR can lead your body into starvation mode, slowing your metabolism and making weight loss more difficult. Knowing your RMR enables you to tailor your calorie intake and exercise regimen effectively, ensuring a sustainable calorie deficit without depriving your body of essential energy.
Furthermore, your RMR may decrease as you lose weight, often causing weight loss plateaus. This decrease occurs because your body needs less energy to maintain a smaller mass, and sometimes, the body adapts by becoming more efficient with calorie utilization. Enhancing your RMR can help you overcome these plateaus and continue progressing towards your weight loss goals.
Three Effective Ways to Boost Your Resting Metabolic Rate

1. Build More Muscle
Strength training is a highly effective method to increase your RMR as muscle tissue burns more calories than fat, even at rest. Including resistance exercises like weightlifting, bodyweight workouts, or resistance band exercises in your routine can enhance muscle mass, thereby elevating your RMR. Aim for at least two to three strength training sessions per week for optimal results.
2. Stay Active Throughout the Day
In addition to structured exercise, maintaining an active lifestyle throughout the day can also elevate your RMR. Activities like walking, standing, or engaging in light movements contribute to your overall energy expenditure and can prevent your metabolism from slowing down during periods of inactivity. Incorporate more movement into your daily routine by taking short walks, using a standing desk, or performing simple stretches during breaks.
3. Consume Adequate Protein
Protein has a higher thermic effect on food (TEF) compared to carbohydrates and fats, resulting in more calories burned during digestion. Moreover, adequate protein intake can help preserve muscle mass during weight loss, preventing the decline in RMR often associated with dieting. Ensure each meal includes a source of lean protein such as chicken, fish, tofu, or legumes.
Boosting your resting metabolic rate is a valuable strategy in your weight loss efforts. By understanding your RMR and implementing strategies to enhance it, you can increase calorie expenditure throughout the day, even without active exercise. Building muscle, staying active, and consuming sufficient protein are three simple yet effective ways to boost your metabolism and support your weight loss objectives.
Remember, achieving sustainable weight loss requires a holistic approach that combines healthy eating, regular physical activity, and a focus on overall well-being.

