How Many Hours Of Sleep Is Healthy?
Imagine a world where the secret to unlocking your full potential lies in something as simple as a good night's sleep. Emerging research continues to highlight the vital role that sleep plays in maintaining both physical and mental health. This naturally leads us to wonder: Just how many hours of sleep is considered healthy for optimal functioning?
Historically, the general recommendation has hovered around 7-9 hours per night for adults. Studies consistently show that getting less than 7 hours regularly can detrimentally affect cognitive performance and overall well-being. With modern life pressing ever more heavily on our schedules, understanding the precise balance between sleep duration and quality becomes increasingly crucial.
The Importance of Sleep on Health
Getting enough sleep is crucial for our overall health. It helps the body repair itself and boosts the immune system. This means fewer sick days and a higher chance of staying healthy.
Sleep also plays a vital role in mental health. Insufficient sleep can lead to mood swings and increased anxiety. It may even contribute to serious conditions like depression.
When we sleep, our brains consolidate information learned during the day. This improves memory and helps us learn new skills. Missing out on sleep can hinder academic performance and concentration.
Finally, sleep affects our physical performance. Athletes often emphasize good sleep to enhance their abilities. Simply put, adequate sleep allows us to function at our best.
Physical Health Benefits of Sleep
Quality sleep is essential for heart health. It helps regulate blood pressure and reduces the risk of heart disease. Poor sleep has been linked to various heart problems.
Strong immunity is another benefit. Those who sleep well are less likely to catch common illnesses like colds. Good sleep strengthens the immune response.
Weight management is influenced by sleep, too. Sleep regulates hunger hormones, reducing the risk of obesity. Bad sleep can lead to unhealthy eating habits.
Mental Health and Sleep
Emotional stability is tied to good sleep. Lack of sleep increases irritability and stress. Regular, restful sleep helps maintain a balanced mood.
For teens and adults, sleep deprivation can lead to severe mental health issues. Anxiety and depression are more common among those who don’t get enough sleep. Simple practices like maintaining a sleep schedule can improve mental health significantly.
Memory and cognitive function benefit from enough sleep as well. When we sleep, the brain processes and stores information from the day. This makes it easier to recall information and make better decisions.
Improving Sleep Hygiene
Creating a bedtime routine can significantly improve sleep quality. Going to bed and waking up at the same time helps the body’s internal clock. This consistency is key for good sleep.
Limiting screen time before bed is also beneficial. The blue light from screens can interfere with melatonin production. Turning off devices an hour before bedtime can help you fall asleep faster.
Lastly, keeping the sleep environment comfortable makes a big difference. A dark, cool, and quiet room is ideal. Investing in a good mattress and pillows can also enhance sleep quality.
The Science Behind Sleep
Sleep is a complex process that our bodies and brains go through each night. It's divided into several stages, each with its unique characteristics. Understanding these stages helps us grasp why sleep is so essential.
Stages of Sleep
Sleep is divided into two main types: Rapid Eye Movement (REM) and Non-REM. Each type of sleep has several stages that the body cycles through multiple times a night. Non-REM sleep includes stages of light and deep sleep, while REM is when dreaming occurs.
Non-REM sleep is crucial for physical restoration. It helps repair muscle tissues and boosts the immune system. This stage is where most of the healing processes happen.
REM sleep is vital for cognitive functions. During REM, the brain processes emotions and memories. This stage is critical for learning and mental health.
The Importance of REM Sleep
During REM sleep, the brain becomes very active despite the body being still. This stage is crucial for emotional regulation and mental well-being. Lack of REM sleep can lead to increased stress and irritability.
Dreaming takes place during REM sleep. It allows the brain to process and organize information. This is why a good night’s sleep can improve memory and problem-solving skills.
REM sleep also influences mood. People who don't get enough REM sleep tend to feel more anxious and depressed. Ensuring adequate REM sleep is essential for a balanced emotional state.
Circadian Rhythms and Sleep
Our bodies follow a natural cycle called the circadian rhythm. This internal clock regulates sleep and wakefulness over a 24-hour period. Light exposure greatly affects this rhythm.
Morning sunlight helps to reset the circadian clock. This is why it’s essential to get some light exposure during the day. At night, dim lighting helps signal the body that it's time to wind down.
Disruptions to the circadian rhythm can lead to sleep disorders. Jet lag and shift work are common examples. Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule helps keep the circadian rhythm balanced.
How Sleep Needs Vary with Age
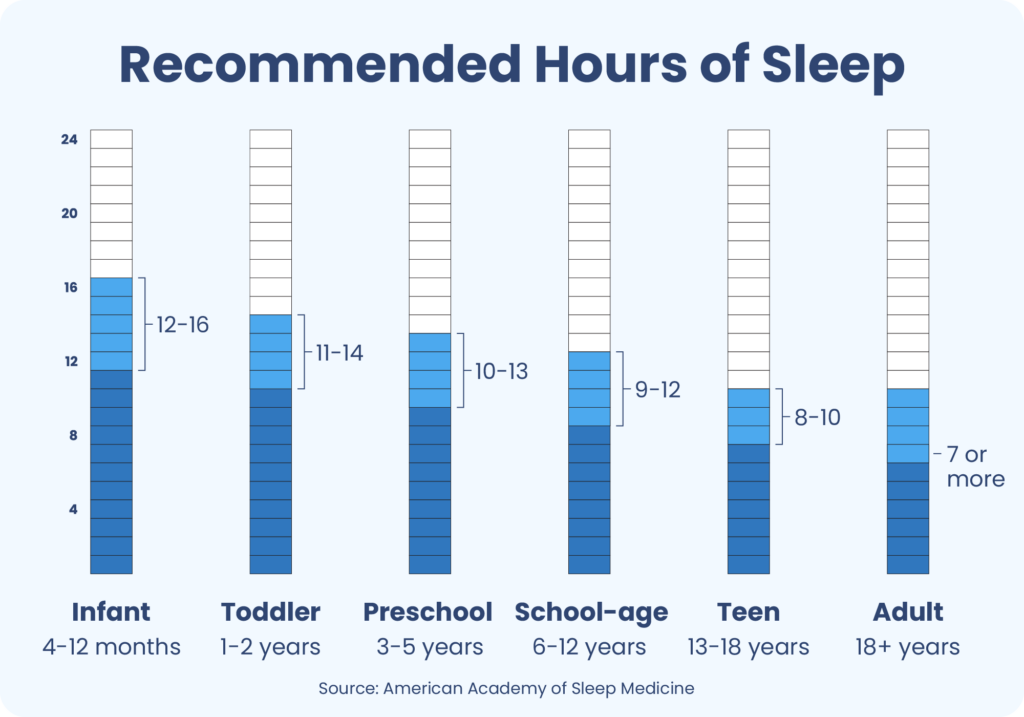
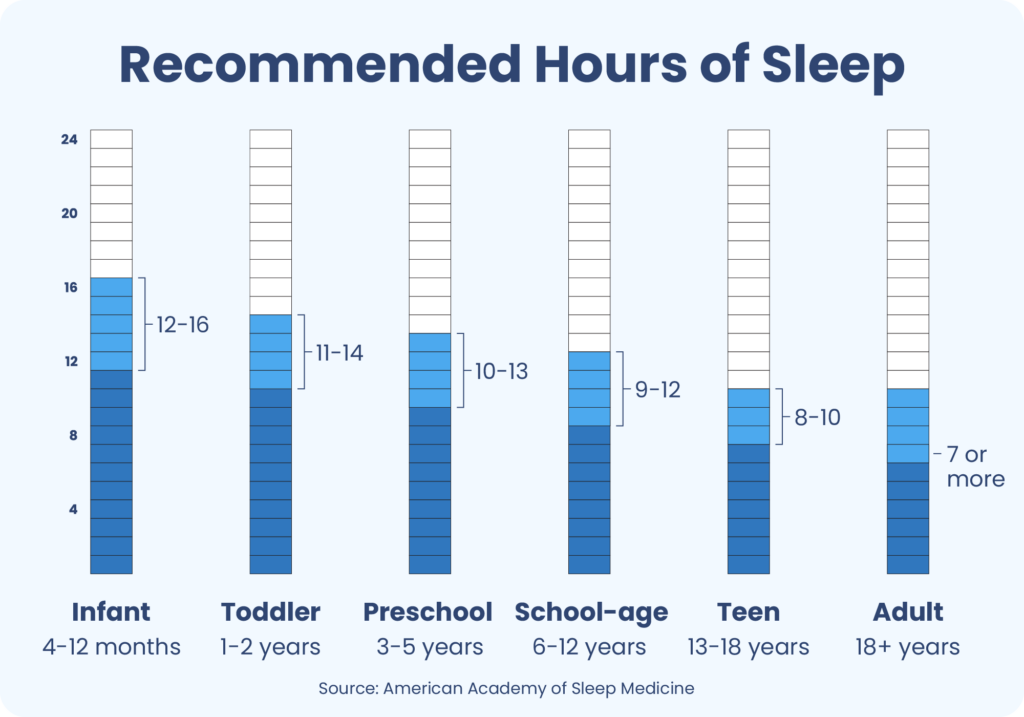
Sleep requirements change as we age. Babies need the most sleep, about 14-17 hours a day. By the time we're adults, the recommended amount drops to 7-9 hours.
Teenagers often require around 8-10 hours of sleep. Their bodies and brains are still developing, which makes extra sleep necessary. However, social and academic pressures can make it hard to get enough rest.
Adults usually need about 7-9 hours of sleep per night. Busy lifestyles often lead to sleep deprivation, affecting both physical and mental health. Prioritizing sleep becomes essential for maintaining overall well-being.
Older adults may experience changes in sleep patterns. They might wake up earlier and have more fragmented sleep. Despite these changes, they still need approximately 7-8 hours of sleep.
Gauging the Right Amount of Sleep
Determining the right amount of sleep can be tricky. While general guidelines suggest 7-9 hours for adults, individual needs can vary. Factors like genetics, lifestyle, and overall health play significant roles.
Listening to your body can help gauge how much sleep you need. If you feel alert and productive during the day, you're likely getting enough rest. Feeling constantly tired or relying on caffeine could be signs of insufficient sleep.
Tracking your sleep patterns can also be useful. Using a sleep diary or a sleep tracking app can provide valuable insights. Recording your sleep quality and durations helps identify patterns and areas for improvement.
Stress and mental health are important considerations. High stress levels can disturb sleep and create a vicious cycle of sleep deprivation and poor emotional health. Practicing relaxation techniques before bed can improve sleep quality.
Work and family responsibilities can also impact sleep needs. Parents and caregivers often experience fragmented sleep, affecting overall rest. In such cases, identifying opportunities for short naps may help.
Lastly, consulting a healthcare professional can offer personalized advice. They can provide guidance based on your unique health profile. It’s especially important if you have chronic sleep issues or experience frequent sleep disruptions.
Impact of Sleep Deprivation
Sleep deprivation affects both physical and mental health. It can lead to serious health issues like heart disease and diabetes. Chronic lack of sleep is linked to a weakened immune system.
Mental health suffers greatly from insufficient sleep. People often experience increased anxiety and depression. Memory and cognitive functions are also impaired, making it hard to focus.
Physical performance declines when you don’t get enough sleep. Athletes, in particular, may see reduced reaction times and endurance. Everyday tasks feel more challenging due to fatigue and lack of coordination.
Sleep deprivation can also contribute to weight gain. Hormones that regulate hunger and appetite are disrupted. This often leads to overeating and unhealthy food choices.
Accidents and mistakes are more likely with poor sleep. Driving while sleep-deprived is as dangerous as drunk driving. Drowsiness impairs judgment and reaction times, increasing the risk of accidents.
Relationships can be strained by sleep deprivation too. Irritability and mood swings make social interactions difficult. Getting enough sleep helps improve patience and communication.
Tips for Quality Sleep
Creating a bedtime routine can significantly improve sleep quality. Try going to bed and waking up at the same time every day. This helps regulate your body's internal clock.
Avoiding screens before bed is essential. The blue light from phones and computers can disrupt sleep. Turning off devices an hour before bedtime can aid in falling asleep faster.
Pay attention to your sleep environment. A cool, dark, and quiet room is ideal for restful sleep. Investing in a comfortable mattress and pillows can also make a big difference.
Limit caffeine and heavy meals before bedtime. Both can interfere with the ability to fall asleep. It's best to avoid these several hours before you go to bed.
Regular exercise can also promote better sleep. However, try not to work out too close to bedtime. Doing so might leave you too energized to fall asleep.
Relaxation techniques can be highly beneficial. Activities like reading, taking a warm bath, or listening to calming music can help unwind. Practicing deep breathing exercises might help improve overall sleep quality.
The Myth of Catching Up on Sleep
Many people believe they can "catch up" on sleep during weekends. This practice often fails to undo the negative effects of sleep deprivation. It may provide temporary relief but doesn’t make up for lost sleep.
Regularly disrupting your sleep schedule can confuse your body's internal clock. This inconsistency makes it harder to fall asleep when you need to. Over time, the irregular pattern leads to chronic sleep issues.
Catching up on sleep might also result in poorer quality rest. Oversleeping can leave you feeling groggy and disoriented. A consistent 7-9 hours each night is more effective for maintaining energy and focus.
It's better to create a regular sleep routine. Aim to go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This steady schedule helps keep your internal clock balanced.
If you miss out on sleep one night, short naps can sometimes help. Limit these naps to 20-30 minutes to avoid interfering with nighttime sleep. Strategic napping can offer a quick boost without disrupting your overall rest pattern.
When to Seek Help
Sometimes, despite our best efforts, sleep issues persist. If you consistently struggle to fall asleep or stay asleep, it might be time to seek help. Ignoring these problems can lead to chronic sleep disorders.
Pay attention to your daytime functioning. Feeling excessively sleepy or needing naps frequently can be signs of sleep problems. Long-lasting fatigue affects your quality of life and overall health.
There are several signs that indicate the need for professional advice:
- Loud snoring or gasping for air during sleep
- Frequent nightmares or sleepwalking
- Difficulty staying awake during the day
- Regular difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep
Consulting a healthcare provider can help identify any underlying issues. They may recommend a sleep study to gather more information. Treatments can range from lifestyle changes to medical interventions.
Ignoring sleep problems can have serious consequences. Untreated sleep disorders increase the risk of other health issues like heart disease and depression. Seeking timely advice helps improve both sleep quality and overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Sleep is vital for our health and well-being. Here are some common questions people have about sleep and how to get enough of it.
1. What are the effects of sleep deprivation?
Long-term sleep deprivation can lead to serious health issues like heart disease, diabetes, and weakened immune function. It also impacts mental health, making people more prone to anxiety, depression, and irritability.
Short-term effects include impaired cognitive function, reduced concentration, and slower reaction times. Lack of sleep can also increase the risk of accidents and errors in daily activities.
2. Why do we dream during sleep?
Dreaming mainly occurs during the Rapid Eye Movement (REM) stage of sleep. This phase is crucial for emotional processing and memory consolidation.
While scientists aren't entirely sure why we dream, it's believed that dreams help us sort through daily experiences. They allow our brains to cope with emotions and stress.
3. How does diet affect sleep quality?
The food we eat can significantly impact our quality of sleep. For instance, consuming caffeine or heavy meals near bedtime can disrupt your ability to fall asleep.
Certain foods like those rich in magnesium or tryptophan may actually promote better sleep. Keeping a balanced diet helps regulate your sleeping patterns naturally.
4. Is napping beneficial for everyone?
Napping can be beneficial if done correctly and at the right time of day. Short naps of 20-30 minutes can boost alertness without affecting nighttime sleep.
However, longer naps or late-afternoon naps might make it harder to fall asleep at night. It's essential to find a balance that works best for each individual.
Conclusion
Understanding how many hours of sleep is healthy is crucial for enhancing our overall well-being. Prioritizing adequate sleep can lead to better mental and physical health, improved concentration, and enhanced emotional stability. It’s essential to recognize that individual needs vary.
By making small adjustments in our daily routines and seeking professional help when needed, we can achieve better sleep quality. This not only improves life expectancy but also elevates our day-to-day performance and happiness. Good sleep is not a luxury; it’s a necessity for thriving in today’s fast-paced world.