How Does Diet And Nutrition Affect Gene Expression?
Imagine if the food you eat could switch your genes on and off, potentially altering your destiny. Such is the profound impact of diet and nutrition on gene expression, a field that’s revolutionizing our understanding of health and disease. Nutrigenomics, the study of how food affects gene behavior, reveals the complex interplay between our diet and our DNA.
Historically, the relationship between diet and gene expression wasn't well understood, but recent discoveries have transformed our perspective. Emerging research suggests that certain nutrients can activate or silence specific genes, potentially reducing the risk of chronic diseases. For instance, folate and other vitamins can modulate genetic pathways that influence metabolism and disease susceptibility.

The Intersection of Diet, Nutrition, and Genes
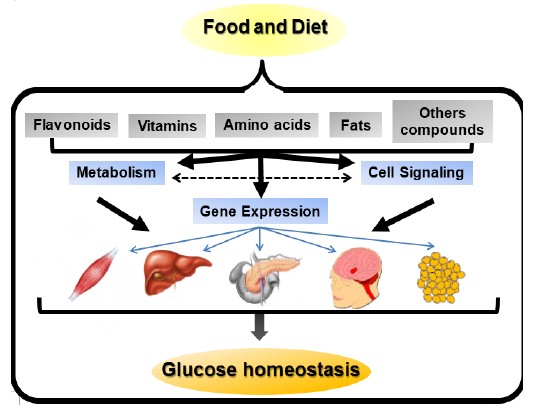
Our genes contain the blueprint for how our bodies work, but this blueprint isn't set in stone. Nutrients from the food we eat can influence gene expression, meaning they can turn certain genes on or off. This interaction is known as nutrigenomics, a field studying how food affects our genes.
For example, vitamins and minerals play a crucial role in gene activity. Eating a diet rich in these nutrients can positively impact the way our genes behave. This connection explains why diet is so important for overall health.
Different foods contain bioactive compounds that can interact with our DNA. These compounds can decrease the risk of diseases by altering gene expression. Foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains are full of these beneficial compounds.
The study of diet, nutrition, and genes is evolving. Personalized nutrition based on genetic makeup is becoming more common. This approach tailors diets to individual genetic profiles, potentially enhancing health outcomes.
The Role of Gene Expression in Health and Illness
Gene expression is how our genes are turned on or off to make proteins needed for various functions. This process is crucial for growth, development, and maintaining health. When gene expression goes wrong, it can lead to diseases.
How Gene Expression Works
Gene expression involves two main steps: transcription and translation. During transcription, DNA is copied into RNA. In translation, RNA makes proteins.
These proteins perform specific functions in the body. By regulating which genes are expressed, the body can adapt to different needs and conditions.
This regulation is vital for normal development and response to environmental changes. Misregulation of gene expression can lead to health issues, including cancer and genetic disorders.
Impact on Chronic Diseases
Gene expression is linked to chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease. Certain genes can be activated by unhealthy lifestyles. This raises the risk of illness over time.
For instance, a diet high in sugar and fat can alter the way genes are expressed. This can lead to insulin resistance and diabetes.
Regular exercise and a healthy diet can positively influence gene expression. This can help prevent chronic diseases and maintain good health.
Environmental Factors and Gene Expression
Environmental factors such as pollutants and stress can affect gene expression. These factors can cause genes to become overactive or underactive. This can result in various health problems.
For example, exposure to cigarette smoke can alter gene expression, leading to lung disease.
Managing environmental factors can improve how genes are expressed. This can enhance overall health and reduce the risk of disease.
Nutrients Influence on Gene Behavior
Nutrients play a significant role in how our genes behave. Specific vitamins and minerals can turn genes on or off, impacting essential body functions. This process is known as gene regulation.
For example, folate, a B-vitamin, can help activate genes involved in DNA repair. This is crucial for preventing mutations that could lead to cancer. Leafy greens and fortified cereals are rich in folate.
Omega-3 fatty acids also affect gene behavior by reducing inflammation. These fats can activate anti-inflammatory genes. Foods like salmon, chia seeds, and walnuts are high in omega-3s.
Phytochemicals, found in fruits and vegetables, can influence gene expression as well. These compounds can enhance the body's defense mechanisms. A diet rich in colorful produce provides a variety of these beneficial nutrients.
Dietary Impact on Epigenetic Changes
Epigenetics refers to changes in gene activity without altering the DNA sequence. What we eat can cause these epigenetic changes, influencing various health outcomes. This process involves adding or removing chemical tags on our DNA.
One way diet affects epigenetics is through methylation. Foods rich in folate and B vitamins can add methyl groups to DNA. This can silence harmful genes, reducing the risk of disease.
The Mediterranean diet, known for its healthy fats and antioxidants, also has epigenetic impacts. This diet can enhance DNA acetylation, which promotes the expression of beneficial genes. Regular consumption of olive oil, nuts, and fish is key.
High-sugar and high-fat diets can cause negative epigenetic changes. These diets can activate genes linked to inflammation and obesity. Avoiding excessive junk food can help prevent these detrimental effects.
Research shows that nutrition during pregnancy can affect the baby's epigenetics. A balanced diet can lead to healthier gene expression patterns in newborns. This highlights the importance of maternal nutrition.
Adopting a nutrient-rich diet can positively influence your epigenome. Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins are excellent choices. These foods can help maintain a healthy gene expression profile.
The Role of Diet in Genetic Disease Risk
Diet plays a crucial role in the risk of developing genetic diseases. Specific foods can activate or deactivate certain genes, affecting whether someone gets a disease. This is why our food choices are so important for health.
For example, a diet high in saturated fats can increase the likelihood of heart disease. These fats can turn on genes linked to inflammation and cholesterol buildup. Reducing these fats can minimize this genetic risk.
Conversely, a diet rich in antioxidants can reduce the risk of genetic diseases. Foods like berries, nuts, and green tea can deactivate harmful genes. These foods are known for their protective effects.
Some people carry genes that make them more susceptible to conditions like diabetes. However, a healthy diet can help manage these risks. It can keep these genes from becoming overactive.
Consuming fiber-rich foods can also positively influence genetic disease risk. Whole grains, fruits, and vegetables help regulate genes involved in metabolism. This can lead to better blood sugar control and lower diabetes risk.
Choosing a balanced diet can have a powerful impact on genetic disease prevention. Nutrient-dense foods can support healthy gene expression. Making wise food choices is essential for long-term health.
Nutrigenetic Testing and Personalized Nutrition
Nutrigenetic testing analyzes your genes to determine how they interact with your diet. This information can help tailor a personalized nutrition plan. The goal is to optimize health based on your genetic makeup.
The test involves collecting a DNA sample, usually through a cheek swab or saliva. This sample is then analyzed in a lab to identify specific genetic markers. These markers can tell you how your body responds to different nutrients.
Based on the test results, you can get recommendations for your diet. For example, if you have a gene that affects how you metabolize fats, your plan might suggest a lower-fat diet. This personalized approach can improve health outcomes.
Nutrigenetic testing is also valuable for managing existing health conditions. If you have genes that increase your risk for certain diseases, specific dietary changes can help mitigate these risks. This makes your diet more effective in promoting health.
Many companies offer nutrigenetic testing services. These services often include consultations with dietitians or nutritionists. Professional guidance can help you implement the personalized recommendations effectively.
Investing in nutrigenetic testing can provide lifelong benefits. Understanding how your genes and diet interact can empower you to make better food choices. This can lead to improved overall health and well-being.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations in Nutrigenomics
Nutrigenomics holds great promise but also faces significant challenges. One of the primary issues is the complexity of gene-diet interactions. Understanding how individual nutrients affect different genes requires extensive research.
Another challenge is accessibility. Nutrigenetic testing and personalized nutrition plans can be expensive. This makes it difficult for everyone to benefit from these advancements.
There are also ethical considerations to address. Privacy is a major concern when dealing with genetic data. Ensuring that this information is secure is crucial.
The potential for misuse of genetic data raises another ethical issue. Companies might exploit this data for profit or without consumer consent. Regulations are needed to protect individual rights.
Additionally, there's a risk of creating dietary recommendations that don't fit everyone. Genetic diversity means one size doesn't fit all in nutrition advice. Personalized plans must be carefully crafted to avoid this pitfall.
Balancing scientific progress with ethical responsibility will determine the future success of nutrigenomics. Researchers, policymakers, and healthcare providers must work together to ensure equitable access and ethical practices.
The Future of Diet and Gene Relationship Study
The exploration of how diet affects gene expression is advancing rapidly. Future research aims to uncover more detailed interactions between specific foods and genes. This could lead to even more precise dietary recommendations.
One promising area is the development of personalized nutrition apps. These apps could use genetic data to create customized meal plans. Imagine having a diet app that tells you exactly what to eat for your unique genetic makeup.
Another exciting development is the potential for gene editing in nutrition. Scientists are exploring ways to alter genes to improve dietary responses. This could revolutionize how we prevent and treat dietary-related diseases.
Collaborative efforts between nutritionists, geneticists, and tech companies will drive future innovations. More comprehensive datasets will enhance our understanding of the gene-diet relationship. These collaborations could lead to groundbreaking discoveries and applications.
Educational programs will also become more important. Schools and communities may start teaching the basics of nutrigenomics. Understanding this science can empower people to make healthier choices.
As research progresses, we can expect to see a greater emphasis on personalized health. The integration of genetics and nutrition will likely become a standard approach in healthcare. This evolution could lead to a healthier, more informed society.
Frequently Asked Questions
The relationship between diet, nutrition, and gene expression is a fascinating area of study. Here are some common questions experts often ask about this topic.
1. What is nutrigenomics?
Nutrigenomics is the study of how food and its nutrients interact with our genes to affect health. This science examines how genetic variations can influence an individual's response to different diets.
By understanding these interactions, scientists hope to develop personalized nutrition plans that optimize health based on one’s genetic makeup. It’s a growing field that promises more tailored dietary recommendations in the future.
2. Can my diet change my genetic information?
Your diet cannot change your underlying DNA sequence; however, it can influence how your genes are expressed. Nutrients from food can add or remove chemical tags on DNA, affecting gene activity.
This process can turn certain genes on or off without altering the actual genetic code. Epigenetic changes like these play a significant role in how your body reacts to various environmental factors, including diet.
3. Which foods have the most impact on gene expression?
Certain foods have compounds known as bioactive molecules that significantly affect gene expression. These include fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and whole grains rich in vitamins and antioxidants.
Foods like fatty fish provide omega-3 fatty acids that also regulate genes involved in inflammation and other metabolic processes. A balanced diet rich in these foods supports healthy gene expression patterns.
4. How can personalized nutrition benefit health professionals?
Personalized nutrition allows health professionals to tailor dietary recommendations based on an individual’s genetic profile. This approach helps optimize nutritional interventions for better patient outcomes.
It reduces trial and error in dietary planning and addresses specific health concerns more effectively by considering unique genetic susceptibilities to certain conditions or nutrients.
5. Are there ethical issues related to nutrigenomic testing?
Yes, several ethical concerns arise from nutrigenomic testing, including privacy and data security issues surrounding personal genetic information. There is also concern about potential misuse of this data by insurance companies or employers.
Moreover, accessibility and equity must be considered since not everyone may afford such testing or its benefits. Ensuring ethical guidelines and regulations are crucial for developing this promising field responsibly.
Conclusion
The intricate relationship between diet, nutrition, and gene expression opens new avenues in personalized healthcare. By understanding how nutrients affect our genes, we can tailor diets to improve health outcomes. This evolving field promises more precise and effective dietary recommendations.
As research advances, the potential for personalized nutrition will continue to grow. Addressing ethical considerations and ensuring equitable access will be crucial. Embracing these advances can lead to a healthier future for all.