Glucose spikes occur when there is an excessive release of sugar into the bloodstream, exceeding the normal range. This can happen when high amounts of carbohydrates are quickly digested and broken down into glucose, leading to a surge in blood sugar levels. These spikes can have detrimental effects on the body, impacting hormonal balance and overall health.
While blood sugar dysregulation is commonly associated with heart disease and diabetes, it can affect even healthy individuals. Monitoring blood sugar levels and minimizing spikes is crucial for maintaining health and supporting hormonal balance.
Glucose spikes can lead to reduced insulin sensitivity, disrupting hormone balance and potentially affecting estrogen levels. Insulin resistance caused by high blood sugar levels can alter estrogen metabolism, leading to hormonal imbalances.
Common symptoms of blood sugar spikes include increased thirst, fatigue, blurred vision, irritability, and intense hunger. Chronic spikes, combined with stress and lack of physical activity, can result in hormone imbalances and various symptoms such as mood swings, weight gain, and sleep issues.
Factors that can cause blood sugar spikes include consuming simple carbohydrates, experiencing stress, inadequate sleep, and dehydration. Simple carbs like white rice and processed foods can quickly raise blood sugar levels, while stress can trigger the release of cortisol, impacting glucose levels. Lack of sleep can affect insulin sensitivity, and dehydration can also contribute to blood sugar spikes.
Insufficient water intake can lead to a decrease in the share of blood volume accounted for by water, resulting in a higher proportion of glucose in comparison.
Dehydration caused by not drinking enough water can concentrate glucose levels in the blood and also impact hormones that regulate blood sugar.
5. Missing Breakfast
It is important to nourish yourself in the morning to properly regulate blood sugar levels throughout the day.
Delaying your first meal until noon can cause blood sugar levels to spike higher after lunch and dinner, according to Seti.
Researchers have observed that skipping breakfast can lead to the liver resisting insulin and producing more glucose, resulting in elevated blood sugar levels after lunch compared to those who did not skip breakfast.
Ways to Control Blood Sugar Spikes
There are several lifestyle changes you can make to reduce glucose spikes.
If you are concerned about how your body is handling blood sugar, it is best to consult a doctor.
Diet
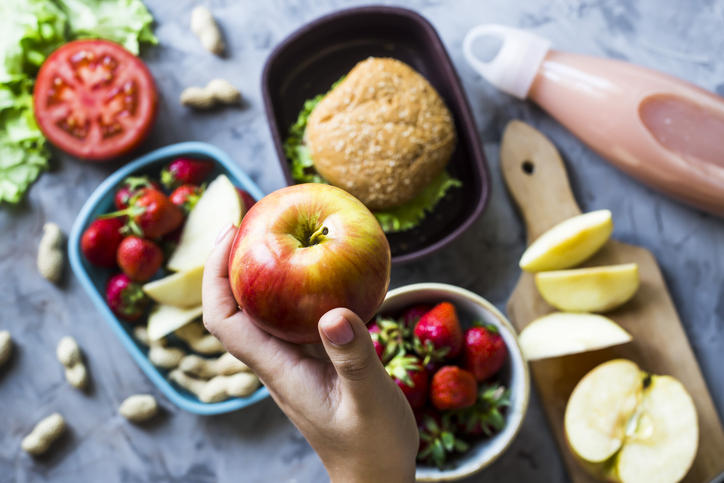

Preventing glucose spikes starts with a balanced diet that limits added sugars and carefully selects energy-providing carbohydrates.
It is important to remember that simple carbs burn quickly and can cause blood sugar spikes, while complex carbs and fiber digest more slowly, maintaining stable postprandial blood sugar levels and providing consistent energy.
Combining macronutrients is also beneficial.
According to Wiemann, "When consuming carbohydrates, it is important to have a source of protein, fat, or fiber along with it. This can help slow the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, preventing blood sugar spikes."
Levine agrees, stating, "You can prevent blood sugar spikes by staying hydrated and eating balanced meals with fiber and protein."
Exercise
Regular exercise is essential for reducing blood sugar spikes in both the short and long term.
Levine explains, "Regular physical activity helps stabilize blood glucose levels by improving insulin sensitivity."
Exercise increases the body's demand for blood glucose to fuel activities and builds muscle tissue to absorb circulating blood sugar efficiently.
Additionally, engaging in physical activity after meals can immediately reduce blood sugar spikes.
Wiemann suggests, "Participating in some form of physical activity shortly after meals can help reduce blood sugar spikes as exercise encourages the body to utilize sugar from the bloodstream for energy."
Sleep
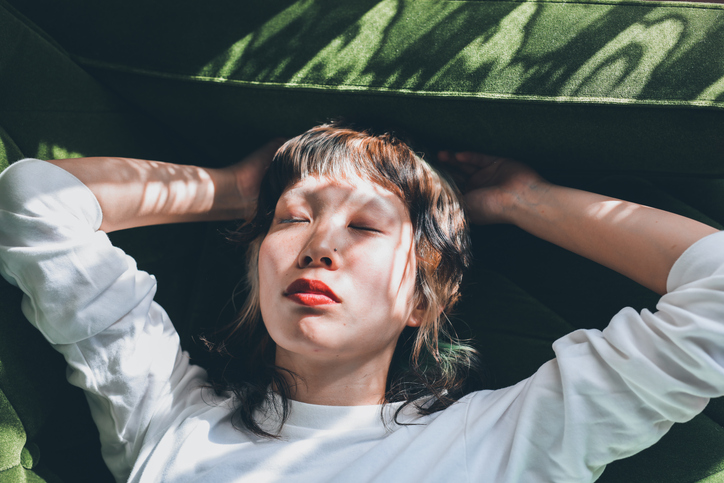

Research indicates that the length, quality, and timing of sleep significantly impact blood sugar levels, which naturally rise in the final hours of sleep to aid in waking up (dawn phenomenon).
Consistently getting around seven hours of sleep per night is associated with improved insulin sensitivity and healthier blood glucose levels.
Adding just one extra hour of sleep per night may help regulate blood glucose levels effectively.
Supplementation
Various vitamins, minerals, herbs, and nutrients can support normal blood sugar levels and minimize the effects of glucose spikes after meals.
Supplements like those found in Belle Vitale Daily Metabolism & Blood Sugar Support can enhance the body's ability to burn fat, maintain healthy metabolism, and support normal blood sugar levels.*
Other supplements can help manage blood sugar levels by addressing stress factors:
Combining adaptogens and essential nutrients in Belle Vitale Daily Hormone & Stress Support can combat the effects of stress, maintain healthy cortisol levels, and support overall hormonal health.*
*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
given sentence in a different way:
"Please remember to bring your ID with you to the event."
Don't forget to bring your ID to the event.