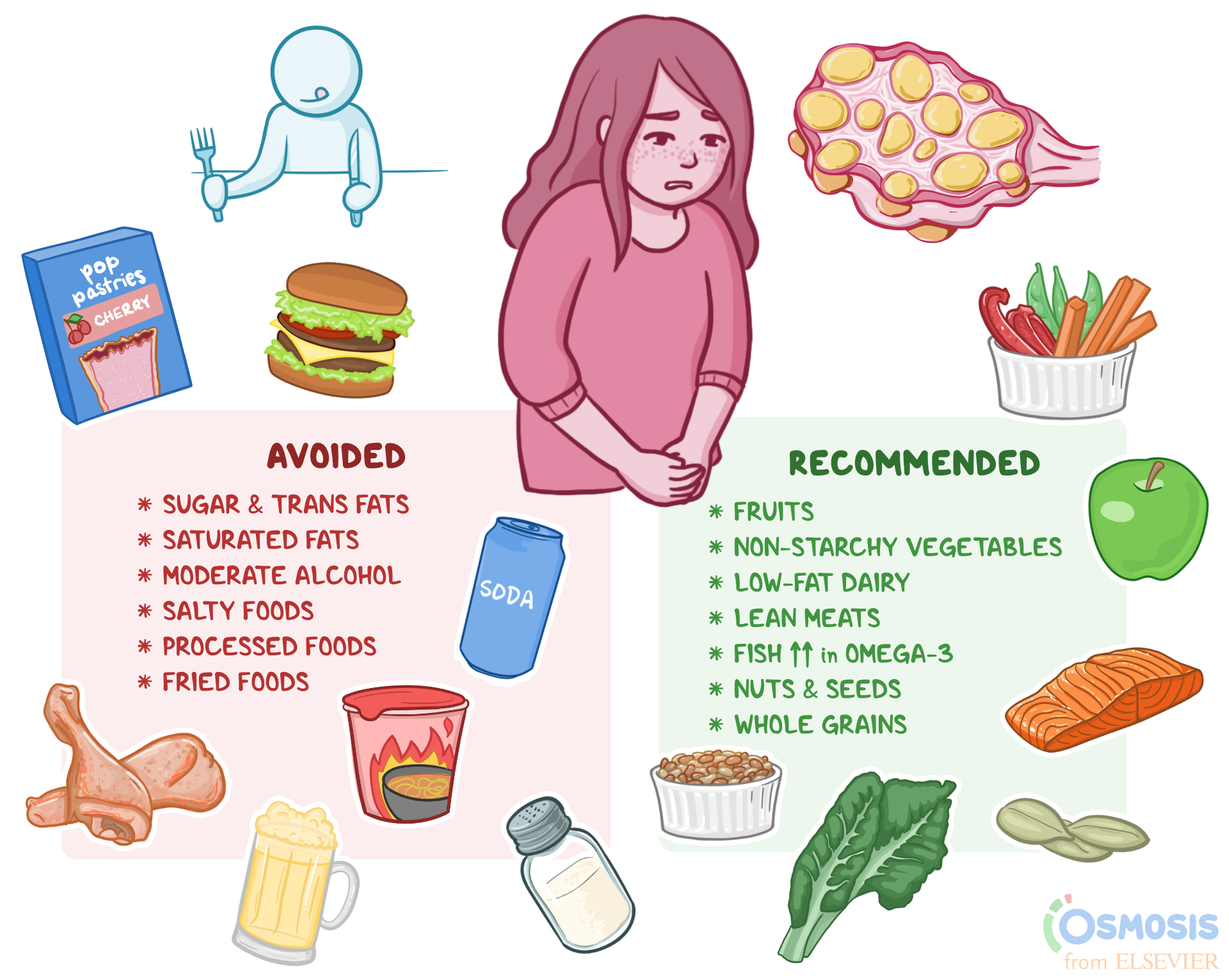
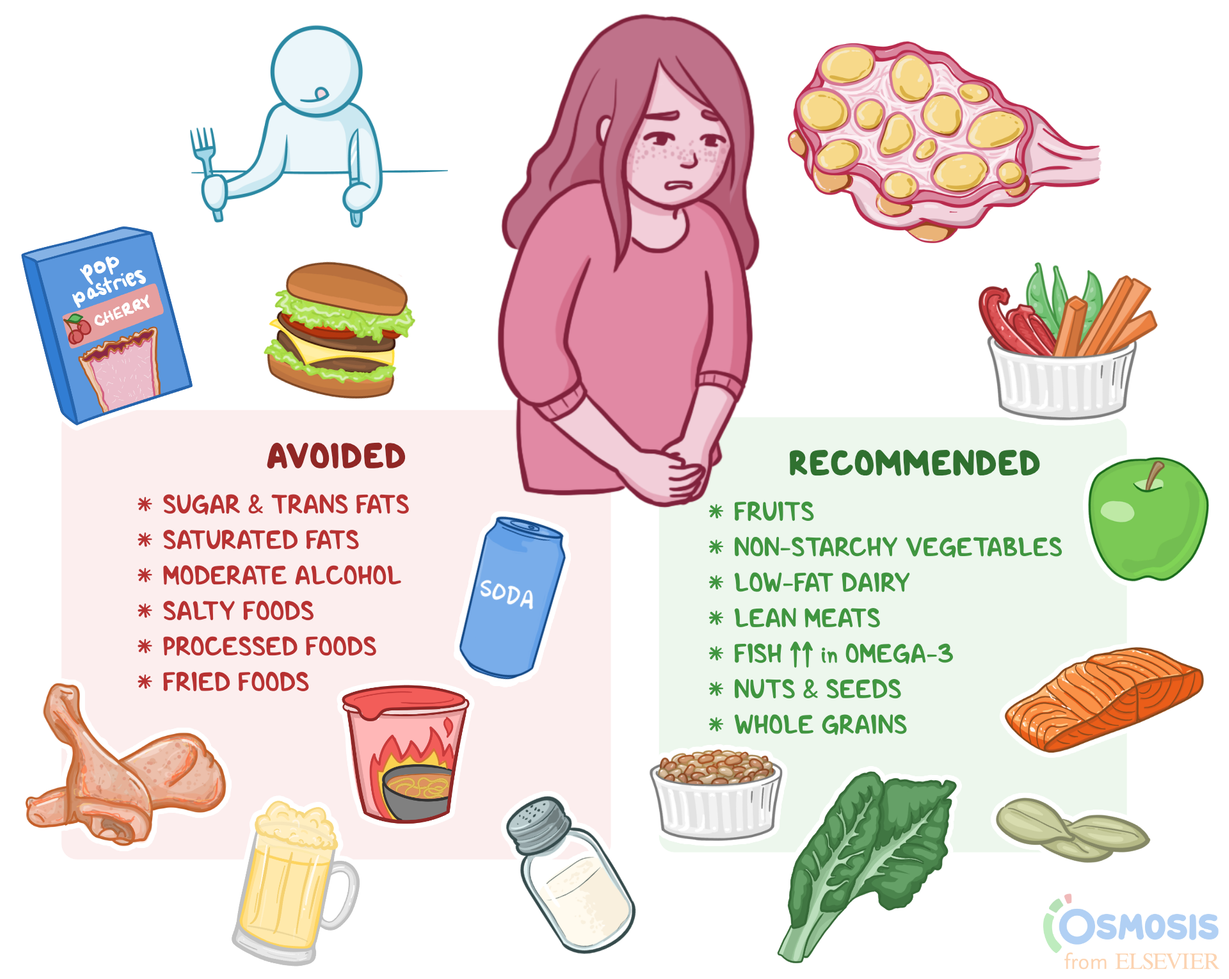
How To Fight Pcos With Diet And Nutrition?
Imagine discovering that nearly 1 in 10 women battle the symptoms of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). For those dealing with this hormonal disorder, diet and nutrition can play a crucial role in managing its symptoms. The intersection of food choices and metabolic health opens a doorway to potentially alleviate some of the toughest symptoms of PCOS.
Historically, a balanced diet that includes low-glycemic index foods has shown promising results in mitigating PCOS symptoms. Research indicates that women with PCOS can benefit significantly from consuming whole grains, fruits, and vegetables while minimizing processed sugars. Moreover, integrating anti-inflammatory foods, such as omega-3 fatty acids, into the diet helps combat insulin resistance, a common issue in PCOS patients.
- Consume a balanced diet rich in whole foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Focus on low-glycemic index foods to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Incorporate healthy fats such as omega-3 fatty acids found in fish and flaxseeds.
- Avoid processed and sugary foods to reduce insulin resistance.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
- Consider taking supplements like inositol, vitamin D, and magnesium after consulting with a healthcare professional.
Understanding PCOS: A Hormonal Disorder
Defining PCOS: Symptoms and Diagnosis
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, or PCOS, is a hormonal disorder affecting 1 in 10 women of reproductive age. It is characterized by irregular menstrual cycles, high levels of male hormones, and cysts on the ovaries. Symptoms can vary widely, making diagnosis challenging.
To diagnose PCOS, doctors typically use a combination of medical history, physical exam, and blood tests. Ultrasound may also be used to look at the ovaries and check for cysts. It's crucial to get a proper diagnosis to manage the condition effectively.
Women with PCOS often struggle with managing their symptoms. Common signs include weight gain, acne, and thinning hair. Early diagnosis can help mitigate long-term complications.
Statistical Overview: How Common is PCOS?
PCOS is one of the most common endocrine disorders in women, affecting roughly 10% of women worldwide. Despite its prevalence, the exact cause of PCOS remains unknown. However, researchers believe that genetics and environmental factors play a role.
Many women may not realize they have PCOS until they experience difficulty getting pregnant. Early intervention can prevent many complications. Lifestyle changes and medication can significantly improve symptoms.
Additionally, underdiagnosis is a significant issue. Many women live with PCOS without realizing it. Understanding the symptoms and seeking medical advice is crucial for effective management.
PCOS Implications: Infertility, Diabetes, and More
Living with PCOS can lead to various health complications beyond fertility issues. Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes are commonly associated with PCOS. Managing blood sugar levels becomes vital for overall health.
PCOS can also increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases. High blood pressure and cholesterol levels are frequently observed in women with PCOS. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is essential to mitigate these risks.
Mental health concerns such as depression and anxiety are also prevalent among women with PCOS. Hormonal imbalances can significantly affect mood and emotional well-being. Support systems and counseling can help manage these challenges.
PCOS and Diet: The Connection
The link between PCOS and diet is strong, affecting how well symptoms are managed. Foods can influence insulin levels, hormone balance, and inflammation. Eating the right foods helps reduce symptoms associated with PCOS.
Insulin Resistance in PCOS: Overview
Insulin resistance is a common issue in women with PCOS. This condition makes it harder for the body to use insulin effectively, leading to higher blood sugar levels. A diet rich in whole grains and fiber can improve insulin sensitivity.
High insulin levels can lead to weight gain, which further complicates the management of PCOS. By choosing low-glycemic index foods, women can help control insulin spikes. Examples include oats, barley, and vegetables.
Managing insulin resistance involves more than just diet. Regular physical activity is important for increasing insulin sensitivity. Combining a balanced diet with exercise can lead to better outcomes.
How Food Affects Hormone Balance
Hormones play a key role in PCOS symptoms, and diet can influence hormone levels. Consuming a diet low in processed foods and high in whole foods helps maintain hormonal balance. Including omega-3 fatty acids can also support hormone health.
Foods high in refined sugars and unhealthy fats can disrupt hormone levels, making symptoms worse. A focus on healthy fats, like those found in avocados and nuts, is beneficial. These fats help regulate hormonal activity.
Protein is another essential component. Balanced protein intake helps stabilize blood sugar and supports hormone production. Sources like lean meats, beans, and quinoa are excellent choices.
The Correlation Between Diet and PCOS Symptoms
Diet can directly impact the severity of PCOS symptoms, such as acne and hair growth. Eating anti-inflammatory foods can reduce these symptoms. Berries, leafy greens, and fatty fish are excellent options.
Weight management is crucial for reducing PCOS symptoms. A diet rich in nutrient-dense foods helps maintain a healthy weight. This, in turn, eases symptoms like irregular periods.
Additionally, staying hydrated is often overlooked but essential. Drinking enough water helps with toxin removal and keeps bodily functions optimal. Adding lemon or cucumber can make hydration more enjoyable.
Mapping Out Your PCOS Diet: Key Principles
Creating a balanced diet is essential for managing PCOS symptoms. Focus on whole, unprocessed foods to maintain stable blood sugar levels and reduce inflammation. This means incorporating plenty of fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins into your meals.
Prioritize low-glycemic index foods that prevent insulin spikes. Whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and oatmeal are excellent choices. These foods not only support blood sugar control but also provide essential nutrients.
Include healthy fats in your diet to help balance hormones. Sources of healthy fats include avocados, nuts, and seeds. These fats can aid in reducing inflammation and supporting overall health.
Hydration is also crucial when managing PCOS. Drinking enough water helps your body eliminate toxins and function properly. Aim for at least 8 cups of water daily, and consider adding lemon or cucumber for extra flavor.
Building a Nutrition Plan for PCOS
Creating a nutrition plan for PCOS begins with balanced meals. Each meal should include a mix of protein, healthy fats, and whole grains. This helps maintain steady energy levels and controls cravings.
Consider starting your day with a protein-rich breakfast. Eggs, Greek yogurt, and smoothies with protein powder are good options. A healthy breakfast sets the tone for the rest of the day.
Focus on portion control to avoid overeating. Using smaller plates can help with this. Pay attention to your hunger cues and stop eating when you’re full.
Snacks should be nutritious and low in sugar. Fresh fruit, nuts, and veggie sticks are excellent choices. Avoid processed and sugary snacks that can cause insulin spikes.
Meal prepping can be a game changer for managing your diet. Preparing meals in advance saves time and reduces the temptation to eat unhealthy foods. Plan your week with balanced meals and snacks.
Keeping a food journal can help track what you eat and how it affects your body. Note down meals, portions, and any symptoms. This information can be invaluable for making adjustments to your diet plan.
Moving Beyond Diet: Exercise and PCOS Management
Exercise plays a key role in managing PCOS symptoms. Regular physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity, which is crucial for those with PCOS. It also helps with weight management and reduces stress levels.
Choosing the right types of exercise is important. Aerobic activities like walking, jogging, and cycling are excellent choices. These activities help burn calories and improve cardiovascular health.
Strength training is another effective exercise for PCOS. Resistance exercises like weight lifting can build muscle and improve metabolism. Aim to include strength training sessions at least twice a week.
Yoga and Pilates are also beneficial for managing PCOS. They help reduce stress and improve flexibility. Practicing mindfulness through these exercises can positively impact mental health.
Consistency is key when it comes to exercise. Incorporate a mix of different activities to keep your routine interesting. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week.
Nutrition Supplements for PCOS: Are They Helpful?
Supplements can play a supportive role in managing PCOS symptoms. They can help address nutritional deficiencies and support hormonal balance. However, they should not replace a healthy diet and regular exercise.
Inositol is a popular supplement for PCOS management. It helps improve insulin sensitivity and can regulate menstrual cycles. Many women report positive effects after incorporating inositol into their routine.
Another useful supplement is omega-3 fatty acids. These healthy fats can reduce inflammation and improve heart health. Sources include fish oil capsules and flaxseed oil.
Vitamin D is also important for women with PCOS. Low levels of vitamin D are common in women with PCOS and can worsen symptoms. Vitamin D supplements can improve insulin resistance and mood.
Magnesium helps with blood sugar control and reduces muscle cramps. Add magnesium-rich foods like nuts and seeds to your diet, or consider a supplement. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any new supplements.
Real-Life Success Stories: Overcoming PCOS with Diet and Exercise
Many women have found success in managing PCOS through diet and exercise. One woman shared how a low-glycemic diet helped stabilize her blood sugar levels. This change led to more regular menstrual cycles.
Another inspiring story involves a woman who incorporated daily yoga into her routine. She reported reduced stress and improved hormone balance. This simple change made a significant difference in her symptoms.
A third success story comes from someone who started weight training twice a week. The strength exercises helped her manage insulin resistance and lose weight. She felt stronger and more energetic.
The following table highlights these stories:
| Name | Dietary Change | Exercise Routine | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sara | Low-Glycemic Diet | N/A | Regular Menstrual Cycles |
| Maya | N/A | Daily Yoga | Reduced Stress, Improved Hormone Balance |
| Lena | N/A | Weight Training Twice a Week | Weight Loss, Better Insulin Sensitivity�Strength, Improved Energy Levelsology-coupled ?>
>rl-
>< ensights',
to’s nee-efflousSumming Up: Your Diet and PCOS ManagementManaging PCOS through diet requires a consistent and balanced approach. Incorporating whole, unprocessed foods can stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce inflammation. Regular meals with a mix of protein, healthy fats, and carbohydrates are crucial. Exercise should complement your diet plan. Combining aerobic activities and strength training boosts insulin sensitivity and supports weight management. Physical activity also helps reduce stress, which can exacerbate PCOS symptoms. Supplements can offer additional support. Inositol, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamin D have shown benefits in managing PCOS. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplements. Success stories show that lifestyle changes can make a significant difference. Women who adopt these dietary and exercise habits report improved symptoms and better overall health. Staying consistent and patient is key to seeing long-term results. A practical approach includes meal prepping and keeping a food journal. This helps track food intake and symptoms, making it easier to adjust your plan. Small, consistent changes can lead to big improvements in managing PCOS. Frequently Asked QuestionsManaging PCOS through diet and nutrition can be challenging. Here are some common questions and answers to help you navigate this journey. 1. What are the best foods to eat for managing PCOS?The best foods for managing PCOS include whole grains, fresh fruits, and vegetables. These foods help maintain stable blood sugar levels and reduce inflammation. Lean proteins like chicken, fish, and legumes are also beneficial. Including healthy fats from avocados, nuts, and seeds can further support hormone balance. 2. How does insulin resistance affect women with PCOS?Insulin resistance makes it difficult for the body to use insulin effectively, leading to higher blood sugar levels. This condition is common in women with PCOS and can worsen symptoms. A balanced diet that includes low-glycemic index foods can improve insulin sensitivity. Regular exercise also plays a crucial role in managing insulin resistance. 3. Can supplements help in managing PCOS symptoms?Yes, certain supplements can aid in managing PCOS symptoms. Inositol is popular for improving insulin sensitivity and regulating menstrual cycles. Omega-3 fatty acids reduce inflammation while vitamin D helps with hormonal balance. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting new supplements. 4. What role does exercise play in managing PCOS?Exercise is essential for managing PCOS as it improves insulin sensitivity and aids weight management. Activities like walking, jogging, and strength training are highly recommended. Regular physical activity reduces stress levels as well, which can exacerbate symptoms of PCOS. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week. 5. How can I stay consistent with my diet plan for PCOS?Staying consistent involves planning ahead by meal prepping and keeping a food journal. This helps track your intake and make necessary adjustments. Setting realistic goals and seeking support from family or friends can also keep you motivated. Small changes over time lead to significant improvements in symptom management. ConclusionIncorporating a well-balanced diet and regular exercise into your routine can make a significant difference in managing PCOS. Whole foods, low-glycemic index items, and healthy fats play vital roles in symptom control. Coupled with supplements as advised by healthcare professionals, these changes offer tangible benefits. Consistency and dedication are key to seeing long-term improvements. Remember, small changes in diet and lifestyle can yield significant results over time. By staying informed and proactive, you are better equipped to manage PCOS effectively. |