8 Types Of Butter And How To Use Them
Imagine the enticing aroma of golden butter melting in a hot skillet, releasing its nutty scent as it prepares to transform simple ingredients into culinary magic. Different types of butter, from cultured to clarified, each bring a unique character to the table. Understanding these varieties can elevate your cooking to new heights.
Cultured butter, dating back centuries, boasts a tangy flavor profile thanks to added bacterial cultures during fermentation. Meanwhile, clarified butter, or ghee, popular in Indian cuisine, offers a high smoke point perfect for frying. Statistics show that using the appropriate butter type can reduce cooking waste by up to 30%, emphasizing the need for knowledge in this buttery domain.
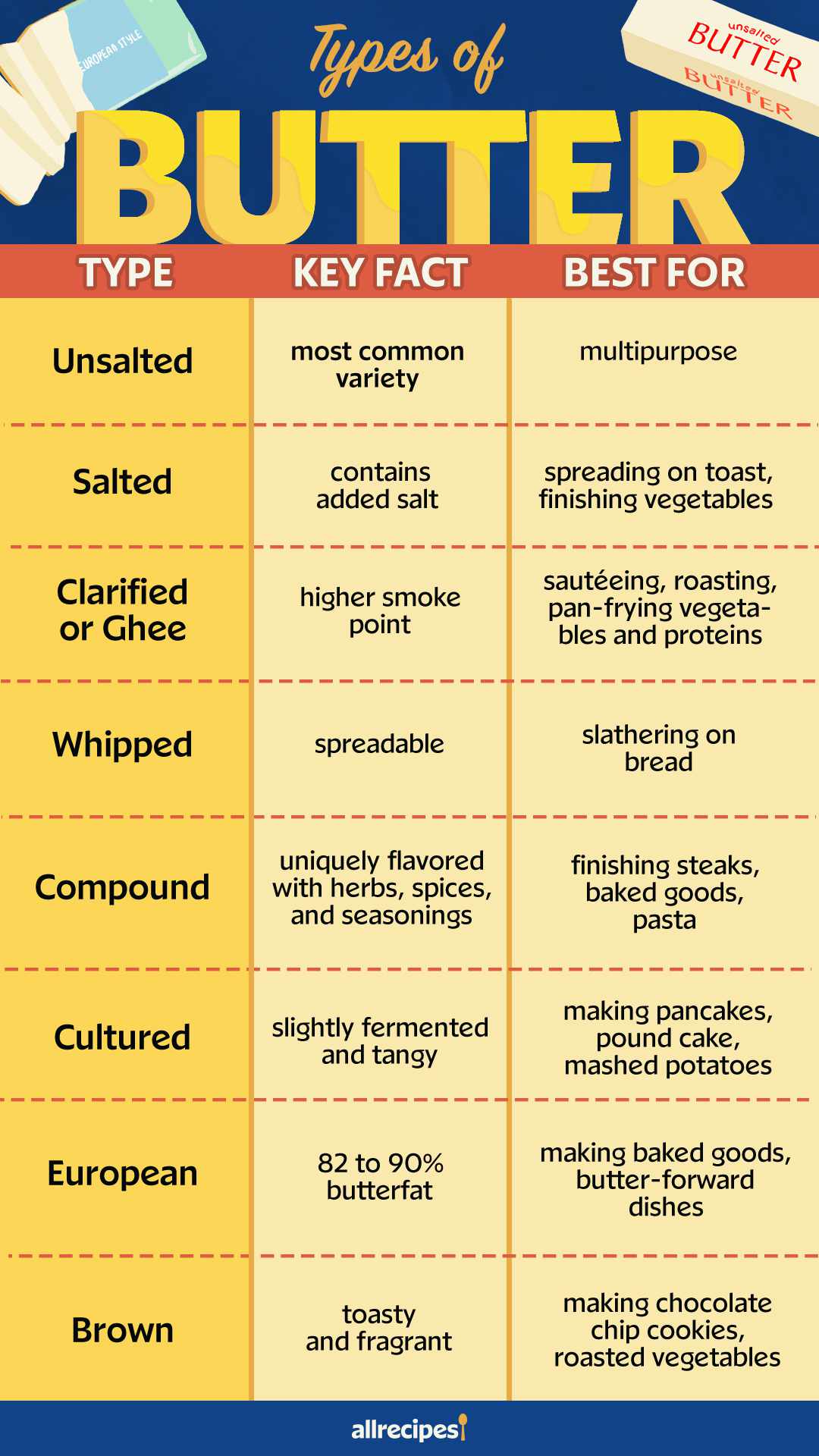
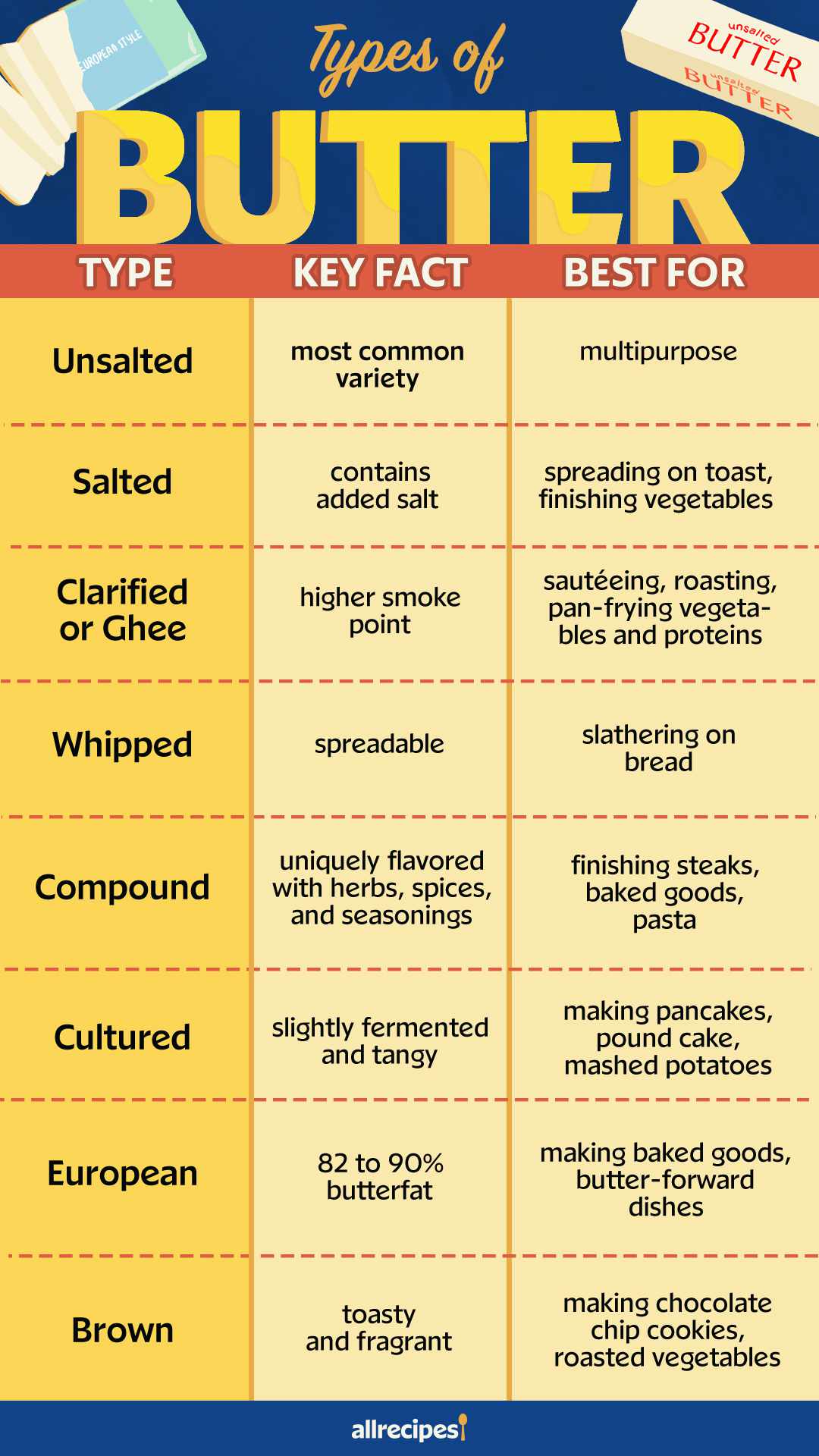
- Unsalted Butter: Ideal for baking and recipes requiring precise salt control.
- Salted Butter: Great for everyday spreading and general cooking.
- Cultured Butter: Adds a tangy flavor, perfect for gourmet dishes.
- Whipped Butter: Easily spreadable, excellent for bread and pancakes.
- European Style Butter: High butterfat content, best for delicate pastries.
- Clarified Butter/Ghee: High smoke point, ideal for frying and sautéing.
- Compound Butter: Mixed with herbs or spices, versatile in enhancing flavors of meats and veggies.
- Grass-Fed Butter: Nutrient-rich with a creamy taste, suitable for health-conscious cooking.
Exploring the World of Butter: Unsalted and Salted Butter
Differences Between Unsalted and Salted Butter
Unsalted butter is simply butter without any added salt. It’s perfect for baking because it gives you control over the amount of salt in your recipe. Salted butter, on the other hand, has salt added during the manufacturing process, giving it a longer shelf life and a different taste.
Many cooks prefer unsalted butter for precise recipes, while salted butter is great for everyday spreading. Salted butter can be a bit tricky in baking, where exact measurements matter. So, always check your recipe to see which type of butter is needed.
How Unsalted Butter is Made
Unsalted butter starts with fresh cream, which is churned until it thickens and butterfat separates from the buttermilk. The butter is then washed and kneaded to remove any remaining buttermilk. Without added salt, this type of butter tastes pure and creamy.
Because there are no preservatives, unsalted butter has a shorter shelf life. It’s usually stored in the fridge and can be frozen for longer storage. Many chefs and bakers favor it for its neutral taste.
Benefits of Using Salted Butter
Salted butter is ideal for spreading on bread, sautéing vegetables, and enhancing flavors in dishes. The added salt acts as a preservative, giving it a longer shelf life. It’s a go-to choice for everyday cooking and convenience.
However, when using salted butter in recipes, the additional salt can affect the overall flavor profile. Always taste and adjust other salty ingredients to ensure the dish isn’t overly salty. For those who enjoy a bit of savory in their butter, salted butter is a tasty choice.
Understanding Cultured Butter and Its Uses
Cultured butter offers a richer flavor profile compared to regular butter. It's made by adding live bacteria cultures to cream before churning. This fermentation process creates a tangy, complex taste that's beloved by many.
How Cultured Butter is Made
The process begins with fresh cream, just like other types of butter. Live cultures are added to the cream and it’s left to ferment for a few hours. Once fermented, it's churned to separate the buttermilk from the butterfat, resulting in cultured butter.
This gives cultured butter its unique tanginess. Farmers and artisans take pride in their cultures, which can vary regionally. The result is a product that is rich, creamy, and full of flavor.
Popular Uses of Cultured Butter
Cultured butter is perfect for spreading on fresh bread, adding an extra layer of flavor. It’s often used in baking to enhance pastries and cookies with its tangy taste. Many chefs also use it to finish sauces and soups, giving dishes a creamy finish.
Additionally, cultured butter pairs well with seafood. Its rich flavor complements the delicate taste of fish and shellfish. It can also be used in compound butters for a gourmet touch.
The Health Benefits of Cultured Butter
Cultured butter contains beneficial bacteria that aid in digestion, thanks to the fermentation process. It’s also rich in vitamins A and K2, which support bone and eye health. Moreover, the tangy flavor often means less salt is needed in recipes, which is great for those watching their sodium intake.
Like any butter, it’s high in saturated fats, so enjoy in moderation. However, its rich creaminess means a little goes a long way. This makes it a delicious and healthy addition to many dishes.
What is Whipped Butter and How to Use It
Whipped butter is made by whipping regular butter to incorporate air into it. This process makes it lighter and easier to spread. The added air gives whipped butter a fluffy, airy texture that is perfect for various applications.
People often use whipped butter as a spread for bread and toast. It’s also a popular choice for topping baked potatoes and pancakes. Because it spreads so easily, it’s a great choice for those who enjoy butter without the hassle of waiting for it to soften.
Whipped butter is created simply by using a mixer to whip regular softened butter. You can add flavorings such as herbs, garlic, or honey. This makes it versatile and customizable for different dishes and tastes.
One significant benefit of whipped butter is that it has fewer calories per serving than regular butter. This is because the air increases the volume without adding more fat. It’s a practical choice for those looking to reduce calorie intake while still enjoying the taste of butter.
European Style Butter: What Sets It Apart
European style butter is known for its rich, creamy texture and higher butterfat content. Unlike regular butter, which typically has 80% butterfat, European style butter contains about 82-85% butterfat. This makes it creamier and gives it a more luxurious mouthfeel.
The secret behind this higher butterfat content lies in the churning process. European style butter is churned longer, which allows more water to be removed. This makes the butter richer and more intense in flavor, which many people prefer for baking and cooking.
Another key difference is that European style butter is often cultured. This means that bacterial cultures are added to the cream before churning, giving the butter a slightly tangy flavor. This tanginess can enhance the taste of baked goods and pair well with savory dishes.
This type of butter typically comes in a thicker block form, rather than the sticks often found in the U.S. It's also a bit more expensive due to the higher quality and specialized production process. However, many chefs and home cooks deem it worth the extra cost for certain recipes.
When should you use European style butter? It's perfect for baking delicate pastries and making creamy sauces. The higher butterfat content helps create flakier pie crusts and more flavorful cookies. It’s also great for spreading on fresh bread to truly savor its richness.
In terms of health benefits, European style butter can be a better option because it's often made from grass-fed cows. This means it contains higher levels of beneficial omega-3 fatty acids and vitamins. Switching to European style butter can enhance both the taste and nutritional value of your dishes.
Diving into Clarified Butter and Ghee
Clarified butter and ghee are both made by simmering butter to separate out the water and milk solids. This process leaves behind pure butterfat. The main difference is that ghee is cooked a bit longer, giving it a nuttier flavor.
Clarified butter is often used in cooking due to its high smoke point. This means it won’t burn as easily as regular butter, making it ideal for frying and sautéing. It's a staple in many professional kitchens.
- High smoke point
- Pure butterfat
- Ideal for frying
Ghee, on the other hand, is a staple in Indian cuisine. It's prized for its rich, nutty taste and the fact that it doesn’t need refrigeration. Ghee can add a unique flavor to dishes like curries and rice.
Both clarified butter and ghee have health benefits, including being rich in vitamins A, E, and K. They also contain butyrate, a fatty acid beneficial for gut health. Ghee is often considered a healthier option due to its additional cooking process.
You can even make them at home. Simply melt butter and simmer it until the water evaporates and the milk solids separate. Strain the solids out, and you have clarified butter. Cook it a bit longer for ghee.
What's Compound Butter and How to Use It at Home
Compound butter is regular butter mixed with additional ingredients like herbs, spices, or even sweet elements. This combination creates a flavorful spread that can enhance many dishes. It’s versatile and easy to make right in your kitchen.
To create compound butter, you start with softened butter and mix in your chosen ingredients. Common options include garlic, parsley, and lemon zest. Once mixed, shape the butter into a log and refrigerate it until firm.
- Garlic and herb compound butter
- Honey cinnamon compound butter
- Blue cheese and chive compound butter
Use compound butter to add flavor to meats, fish, and vegetables. A slice of garlic herb butter melting over a steak can be truly mouthwatering. It’s also fantastic on baked potatoes and fresh bread.
For dessert, try a sweet version with honey and cinnamon to spread on muffins or pancakes. This can turn a basic breakfast into something special. Experiment with different flavor combinations to find your favorites.
Making compound butter is quick and straightforward. You can even prepare it in advance and freeze it for later use. Having a variety of compound butters on hand can make meal prep easier and more delicious.
Richness of Grass-Fed Butter
Grass-fed butter is made from the milk of cows that graze on grass. This results in a richer flavor and more vibrant yellow color compared to regular butter. The nutrient profile of grass-fed butter is also more beneficial.
One major benefit is the higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids. These healthy fats are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. They support heart health and can improve brain function.
- Elevated omega-3 levels
- Rich in vitamins A, D, E, and K
- Naturally yellow due to beta-carotene
The high content of vitamins A, D, E, and K makes grass-fed butter a nutritional powerhouse. Vitamin A supports vision and skin health, while vitamin K helps with blood clotting. The beta-carotene gives the butter its natural yellow hue.
This type of butter is also praised for its flavor. It's richer and creamier because of the cow's diet. This enhanced taste can elevate your cooking and baking.
Grass-fed butter can be used just like regular butter but brings added benefits. Use it for spreading, baking, or sautéing to enhance both flavor and nutrition. Your dishes will taste better and be better for you!
Light Butter: A Healthier Alternative?
Light butter is designed to be a lower-calorie option, making it popular among those looking to cut down on fat. It is made by incorporating water and sometimes other ingredients to reduce fat content. This results in a spread that has about half the calories of regular butter.
One of the main benefits of light butter is its lower calorie count. For people watching their weight, this can be a significant advantage. You can enjoy the taste of butter without consuming too many calories.
- Lower in calories
- Less fat
- Often includes added water
Light butter can be used in similar ways to regular butter. It’s great for spreading on toast or using as a topping for vegetables. However, it’s not ideal for baking because the added water can affect the texture of baked goods.
While light butter is a good option for those looking to reduce fat intake, it's essential to read the label. Some brands may include added ingredients like emulsifiers or preservatives. Choosing a brand with minimal additives is always the best choice.
Overall, light butter offers a way to enjoy the flavor of butter with fewer calories and less fat. It’s a handy alternative for everyday use, but keep its limitations in mind when cooking and baking. Enjoy it in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
Frequently Asked Questions
Butter is a versatile ingredient in many kitchens. Here are some frequently asked questions to help you understand more about different types of butter and their uses.
1. What makes cultured butter different from regular butter?
Cultured butter has live bacterial cultures added to the cream before churning, giving it a tangy flavor. Regular butter does not contain these live cultures and has a milder taste.
This unique process also adds complexity to cultured butter's flavor profile, making it richer. Chefs love using it to elevate the taste of baked goods and gourmet dishes.
2. How do you make compound butter at home?
You can create compound butter by softening regular butter and mixing in your choice of herbs, spices, or sweeteners. Common additions include garlic, parsley, lemon zest, or honey.
Once mixed thoroughly, shape the butter into a log and refrigerate until firm. This homemade touch adds unique flavors to meats, vegetables, and bread.
3. Why is European style butter ideal for baking pastries?
European style butter has a higher butterfat content than standard American butter, typically around 82-85%. This extra fat gives it a creamier texture that’s perfect for achieving flaky pastries.
The rich flavor also enhances the taste of baked goods like croissants and cookies. Many pastry chefs prefer it for this reason.
4. What are the health benefits of grass-fed butter?
Grass-fed butter contains higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids compared to regular butter. These healthy fats support heart health and reduce inflammation.
This type of butter is also rich in vitamins A, D, E, and K2. These nutrients are essential for vision, bone health, and immune function.
5. Can I use light butter as a substitute in all recipes?
Light butter works well as a spread on toast or topping vegetables due to its lower calorie count. However, it’s not ideal for baking as it contains more water than regular butter.
The extra moisture can affect the texture and consistency of baked goods like cookies or cakes. For best results in baking recipes, stick to full-fat butters.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of butter and their uses can significantly elevate your culinary skills. Each variety, from cultured to grass-fed, brings unique flavors and benefits to your recipes.
Whether you’re baking delicate pastries or preparing a simple sauté, choosing the right butter can make all the difference. Exploring these options allows you to experiment and find what best suits your cooking needs.